* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Securing Information Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
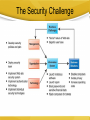
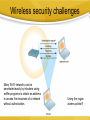
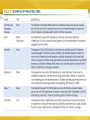
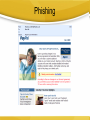
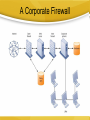
C8- Securing Information Systems Facebook Virus Update your Adobe Flash! Security and Control *** The Security Challenge Security Vs. Control • Security: the policies, procedures and technical measures used to prevent unauthorized access, alteration, threat or physical damage to information systems • Controls: methods to ensure the safety of assets, reliability of records and adherence to standards Security- Vulnerabilities The potential for unauthorized access, abuse, or fraud is not limited to a single location but can occur at any access point in the network. Smart Phones 8-5 System Vulnerability and Abuse Internet vulnerabilities • Vulnerable to outside attacks • Abuses can have widespread impact • E-mail increases system vulnerability • Fixed IP Address- they know where you are! • VOIP Service Vulnerabilities 8-6 Wireless security challenges Many Wi-Fi networks can be penetrated easily by intruders using sniffer programs to obtain an address to access the resources of a network without authorization. Using the rogue access points!!! Malicious Software (Malware) • Computer viruses: – Rogue software programs that attach to other programs in order to be executed, usually without user knowledge or permission – Deliver a “payload” – Can spread by email attachments • Worms: – Programs that copy themselves from one computer to another over networks- rely less on human to spread – Can destroy data, programs, and halt operation of computer networks • Trojan Horse: • A software program that appears to be benign, but then does something unexpected • Often “transports” a virus into a computer system System Vulnerability and Abuse 8-8 Malware … • SQL injection attacks • Spyware – install themselves surreptitiously to monitor user Web surfing activity/ serve advertising. – Keyloggers Hackers & Cybervandalism • Hackers: individuals who attempt to gain unauthorized access to a computer system • Cracker: a hacker with criminal intent • System intrusion, theft of goods and information, system damage and cybervandalism – Cybervandalism: intentional disruption, defacement, or destruction of a Web site or system System Vulnerability and Abuse 8-11 Spoofing and Sniffing • Spoofing – masquerading as someone else, or redirecting a Web link to an unintended address • Sniffing – an eavesdropping program that monitors information travelling over a network System Vulnerability and Abuse 8-12 DoS Attacks • Denial of Service • Hackers flood a server with false communications in order to crash the system Use thousands of “zombie” PCs infected with malicious software without their owners’ knowledge and organized into a botnet. System Vulnerability and Abuse 8-13 Computers As Targets Of Crime • Breaching the confidentiality of protected computerized data • Accessing a computer system without authority • Knowingly accessing a protected computer to commit fraud • Intentionally accessing a protected computer and causing damage, negligently or deliberately • Knowingly transmitting a program, program code or command that causes damage to it • Threatening to cause damage to a computer 8-16 Computers As Instruments Of Crime • Theft of trade secrets • Unauthorized copying of software or copyrighted intellectual property,s uch as articles, books, music, and video • Schemes to defraud • Using e-mail for threats or harassment • Intentionally attempting to intercept electronic communication • Illegally accessing e-mail and voice mail • Transmitting or possessing child pornography Computer Crime • Identity theft – A crime in which the imposter obtains key pieces of personal information – Phishing- Setting up fake Web sites or sending email messages that look legitimate, and using them to ask for confidential data – Eviltwins are wireless networks that pretend to offer trustworthy Wi-Fi connections to the Internet, such as those in airport lounges, hotels, or coffee shops. – Pharming redirects users to a bogus Web page, even when the individual types the correct Web page address into his or her browser. 8-16 Computer Crime … • Click Fraud • Cyberterrorism and Cyberwarfare – Exploitation of systems by terrorists • Internal Threats: Employees – lack of knowledge is the single greatest cause of network security breaches • Software vulnerability – bugs or program code defects- virtually impossible to eliminate all bugs from large programs. – Patches- To correct software flaws vendor creates small pieces of software called patches 8-16 Phishing Business Value of Security and Control • Different govt. regulations/acts • Protect own information assets and customers, employees, and business partner • legal liability – litigation for data exposure or theft • A sound security and control framework= high return on investment 8-18 Computer forensics • is the scientific collection, examination, authentication, preservation, and analysis of data held on or retrieved from computer storage media in such a way that the information can be used as evidence in a court of law. – Recovering data from computers while preserving evidential integrity – Securely storing and handling recovered electronic data – Finding significant information in a large volume of electronic data – Presenting the information to a court of law Establishing a Framework • General controls – The design, security, and use of computer programs and the security of data files in throughout the organization’s IS infrastructure. – Include software controls, physical hardware controls, computer operations controls, data security controls, controls over implementation of system processes, and administrative controls. • Application controls – unique to each application, like payroll – (1) input controls, (2) processing controls, and (3) output controls 8-20 Establishing a Framework … • Risk Assessment Chief Security Officer (CSO) – Determine level of risk to the firm in the case of improper controls • Security policy – ranking information risks, identifying acceptable security goals, and identifying the mechanisms for achieving these goals. – Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) • defines unacceptable and acceptable actions – Identity Management • of business processes and software tools for identifying the valid users of a system and controlling their access to system resources. 8-20 Two security profiles or data security patterns Access rules for different levels of users in the human resources function. Establishing a Framework … • Disaster recovery planning – duplicate computer center • Business continuity planning – – – – Fault-tolerant computer systems High-availability computing Recovery-oriented computing Security outsourcing • Auditing – An MIS audit examines the firm’s overall security environment as well as controls governing individual information systems. 8-20 Technologies And Tools • Access controls – Consist of all the policies and procedures a company uses to prevent improper access to systems by unauthorized insiders and outsiders • Authentication – ability to know that a person is who she or he claims to be • Passwords, tokens, biometric authentication • Biometric authentication uses systems that read and interpret individual human traits, such as fingerprints, irises, and voices, in order to grant or deny access. Firewalls • Firewalls: Hardware and software controlling flow of incoming and outgoing network traffic – Packet Filtering examines selected fields in the headers of data packets flowing back and forth from network and the Internet – Stateful inspection provides additional security by determining whether packets are part of an ongoing dialogue between a sender and receiver – Application proxy filtering- examines the application content of packets. A proxy server stops data packets originating outside the organization, inspects them, and passes a proxy to the other side of the firewall. ………………. A Corporate Firewall Intrusion Detection Systems, and Antivirus • Intrusion Detection Systems – Full-time monitoring tools placed at the most vulnerable points of the corporate networks to detect and deter intruders • Antivirus and Antispyware • Unified Threat Management Systems – combined into a single appliance various security tools, including firewalls, virtual private networks, intrusion detection systems, and Web content filtering and antispam software. Technologies And Tools For Security And Control 8-27 Improve Security • Wi-Fi Network – Setting • HTTPS• SSL/TLS- secure connection Mail/Message Encryption Encryption • Encryption-rmvtu[yopm-fodszqujpo – Coding and scrambling of messages to prevent unauthorized access to, or understanding of, the data being transmitted • Public key encryption: – Uses two different keys, one private and one public. The keys are mathematically related so that data encrypted with one key can be decrypted using only the other key • Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): – Use of public key cryptography working with a certificate authority Technologies And Tools For Security And Control Public Key Encryption A public key encryption system can be viewed as a series of public and private keys that lock data when they are transmitted and unlock the data when they are received. The sender locates the recipient’s public key in a directory and uses it to encrypt a message. The message is sent in encrypted form over the Internet or a private network. When the encrypted message arrives, the recipient uses his or her private key to decrypt the data and read the message. Technologies And Tools For Security And Control 8-31 Ensuring System Availability Solution Guidelines • Security and control must become a more visible and explicit priority and area of information systems investment • Support and commitment from top management is required to show that security is indeed a corporate priority and vital to all aspects of the business • Security and control should be the responsibility of everyone in the organization Management Opportunities, Challenges, And Solutions Learning Objectives • Analyze why information systems need special protection from destruction, error, and abuse. • Assess the business value of security and control. • Design an organizational framework for security and control. • Evaluate the most important tools and technologies for safeguarding information resources. 8-35