* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Brain - Peoria Public Schools
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
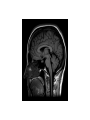
The Human Brain Option A.2 The anterior part of the neural tube expands to form the brain. • Define cephalizationa. The development of the head region. • State the number of neurons in the human brain. a. 86 Billion • Describe the advantage of having a brain. a. Communication between the billions of neurons is more rapid than if the control centers are spread out. Different parts of the brain have specific roles. • State the function of the following regions of the brain: a. Medulla oblongata- deals with involuntary functions such as heart rate and breathing. b. Cerebellum- important in motor control, posture, balance, some cognitive function such as speech. Different parts of the brain have specific roles. c. Hypothalamus- interface between the brain and the pituitary gland, hormones, homeostasis. d. Pituitary Gland1. Posterior Lobe- stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus. 2. Anterior Lobe- releases hormones e. Cerebral Hemispheres- integrating center for higher functions: learning, memory, emotions. The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary process in the body using centers located in the medulla oblongata. • Describe the peripheral nervous system. a. Made of all the nerves outside of the central nervous system. • List the two parts of the peripheral nervous system. a. Voluntary and autonomic • Compare and contrast the two parts of the peripheral nervous system. a. They are both part of the peripheral nervous system but autonomic controls involuntary functions and is divided into two parts. The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary process in the body using centers located in the medulla oblongata. • List the two parts of the autonomic nervous system. a. Parasympathetic and sympathetic • Explain how these two parts work together. a. They have opposite effects on the body. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) controls homeostasis and the body at rest and is responsible for the body's "rest and digest" function. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) controls the body's responses to a perceived threat and is responsible for the "fight or flight" response.