* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grade 10 Unit Breakdown
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
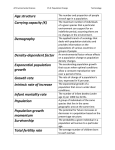
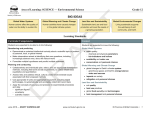
Dave’s Science Course breakdown tables Science Academic 10 Biology Unit Big Ideas Tissues, Organs and Systems of Living things Plants and animals, including humans, are made of specialized cells, tissues, and organs that are organized into systems. Developments in medicine and medical technology can have social and ethical implications. Basic Concepts Problems/Inquiry Cell cycle and Microscope Usage Mitosis (mitosis, plant and animal cells, Cell specialization specialized cells Animal systems and (muscle, nerve, their interaction with xylem, red blood each other cells) Terminology Dissection of worm, associated with fish or frog. topics above STSE Controversial issues in biology (i.e. stem cell research, cloning) Medical Technology (X-rays, MRI, Nuclear resonance imaging…) Public Health Strategies (i.e. vaccination clinics) Chemistry Unit Big Ideas Chemical Reactions Basic Concepts Simple Nomenclature (ionic, polyatomic, acids and molecular compounds) Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations Physical vs. Chemical Change (signs of chem.. change) pH scale Terminology associated with topics above Problems/Inquiry STSE Synthesis, Safety and decomposition, Environmental neutralization and issues associated displacement with chemical reactions reactions (i.e. use of chlorine in pools) Classifying substances as Analyse how acids/bases/neutrals understanding the using pH paper or properties of a acid-base indicators substance and their reactions can be Chemical change lab applied to solving Law of conservation environmental of mass issues (i.e. Model building to chemicals used to show reactions treat oil spills) Chemicals react with each other in predicable ways. Chemical reactions may have a negative impact on the environment, but they can also be used to address environmental change. Dave’s Science Course breakdown tables Physics Unit Big Ideas Light and Geometric Optics Basic Concepts Types of Light Emissions Electromagnetic Spectrum Reflection/Refraction Properties of Light and how they cause natural phenomena Ray Diagrams and the associated math to predict image position and characteristics from different lenses and mirrors Laws of Reflection Terminology associated with the above topics Problems/Inquiry Image Positions using ray diagrams and curved/flat mirrors and lenses Light Refraction from one medium to another, qualitative and quantitative observations, calculate the indices of refraction, determining trends as light passes through different media Light has characteristics and properties that can be manipulated with mirrors and lenses for a range of uses. Society has benefited from the development of a range of optical devices and technologies. STSE Technological devices that use mirrors and lenses (i.e. telescope) Technological devices that use the properties of light (i.e. camera) Technological devices that alter human perception of light (i.e. night vision goggles, laser eye surgery…) Dave’s Science Course breakdown tables Earth and Space Unit Big Ideas Climate Change Basic Concepts Climate change (causes and indicators, is it really happening?) Greenhouse Effect (natural vs. human, causes and effects) Heat transfer (ocean currents) Earth’s Climate system (sun, oceans, etc...) Canadian Climate zones How water affects climate Terminology associated with the above topics Problems/Inquiry STSE Heat transfer lab Climate change and the positive-negative Build a model to effects it is having show the greenhouse on human activity effect and natural systems Assess the effectiveness of current initiatives aimed at curbing climate change (i.e. Energy Star appliances, Drive Clean fuel…) Earth’s climate is dynamic and is the result of interacting systems and processes. Global change is influenced by both natural and human factors. Climate change affects living things and natural systems in a variety of ways. People have the responsibility to assess their impact on climate change and to identify effective courses of action to reduce this impact. Dave’s Science Course breakdown tables Science Applied 10 Biology Unit Big Ideas Tissues, Organs and Systems All animals are made of specialized cells, tissues and organs that are organized into systems. Although technology and chemicals can be used to improve human health, they can also constitute a health hazard. Basic Concepts Problems/Inquiry Cell Cycle and Dissection Mitosis (cancer cells Microscope work vs. non-cancerous (specialized cells, cells) mitosis) Specialized cells (neurons, muscle cells) Organization of the body from cells to organ systems Systems of the body, their functions and their interaction with one another Health problems Terminology associated with the above topics STSE Medical imaging technology Technology and its effect on human health (i.e. cell phones, pesticides, vitamins…) Dave’s Science Course breakdown tables Chemistry Unit Chemical Reactions and their practical applications Big Ideas Chemicals react with one another in predictable ways. Chemical reactions are a necessary component of chemical products and processes used in the home and workplace. Basic Concepts Chemical formulae and naming of simple ionic and molecular compounds Writing and Balancing equations pH scale and neutralization Law of Conservation of Mass Types of Reactions Terminology associated with the above topics Problems/Inquiry Neutralization (as seen in household products (i.e. antacids) and in a lab setting (i.e. HCl and NaOH)) Classifying substances as acids, bases or neutrals using pH paper or acid-base indicators] Law of Conservation of Mass Types of Reactions Molecular models Physics Unit Big Ideas Light and Application of Optics Basic Concepts Refraction, reflection, absorption, transmission Subtractive and Additive Colour Theories Laws of Reflection Electromagnetic Spectrum Types of light emission Terminology associated with the above topics Problems/Inquiry Build an optical device using mirrors Colour theory lab Qualitative characteristics of images using mirrors and lenses as well as ray diagrams (POEs) Refraction of light STSE Chemical reactions and their creation of selected products (i.e. carbonated beverages, rust proofing) Identify chemical reactions used in some professions and assess their health/safety impact (i.e. fire-fighting) A wide range of technologies utilize the properties of light and colour. The behaviour of light depends on the materials with which it interacts. Light is a form of energy, produced from a variety of sources, and can be transformed into other useful forms of energy. STSE Technology that uses the properties of light and/or colour (i.e. stop lights) Describe the role of optical technologies and their effect on information transmission (i.e. satellites, cell phones) Dave’s Science Course breakdown tables Earth and Space Unit Big Ideas Earth’s Dynamic Climate Basic Concepts Global Climate Change (indicators, is it happening?, causes and effects, tools used to assess it) Greenhouse Effect Heat sinks and heat transfer Components of Earth’s climate system Terminology associated with the above topics Problems/Inquiry Carbon footprint How different factors affect global warming Global climate change is affected by both natural and human factors. Climate change affects living things and natural systems in a variety of ways. STSE Sources of greenhouse gases Assess human activities that have increased or decreased greenhouse gas emission How climate change has affected natural systems and human activity