* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO 212 SI Kukday--Energetics (2) Review 2/7
Survey
Document related concepts
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
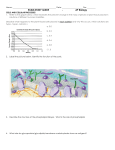
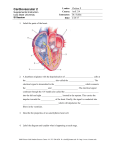
Energetics (2) Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Caleb I. BIOL 212 Dr. Kukday 2/07/2017 1.) Vocabulary Review- Match the Terms & Definitions: a. Binding to the enzyme at a spot i. Activators ______ different from the active site to ii. Inhibitors ______ control activity iii. Krebs Cycle ______ b. Use positive allosteric iv. Aerobic Respiration ______ regulation to enable enzymatic v. Allosteric Regulation ______ activity vi. Electron Transport Chain ___ c. O2 vii. The final electron acceptor__ d. Use negative feedback to viii. Anaerobic Respiration ____ slow/stop enzymatic activity ix. Feedback Inhibition ______ e. Respiration done in the presence x. Irreversible inhibition______ of oxygen xi. Glycolysis ______ f. Blocking an enzyme as a result of feedback g. The process that turns acetyl CoA into NADH and FADH2 h. This process happens outside the mitochondria and turns glucose into pyruvate i. Inhibition that requires making a new enzyme to resume the process j. Process where most of the ATP is actually produced in the mitochondria k. Creating ATP in the absence of oxygen 2.) Can you predict the consequences of mutations in an enzyme that is part of a metabolic pathway? ----- Predict what would happen if the enzyme between pyruvate and acetyl CoA were inhibited. Predict what would happen if the final product of the TCA cycle inhibited the enzyme that turns pyruvate into lactate: 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu 3.) Can you identify types of enzyme regulation (emphasis on feedback inhibition)? ----Label the reaction types below as either “normal reaction”, “competitive inhibition” or “noncompetitive inhibition”. Also label the active site, the allosteric site and the substrate: 4.) Can you compare aerobic and anaerobic respiration pathways with respect to differences in products and energy intermediates produced? ----- Draw the overall products and reactants of cellular respiration. Balance the equation accordingly. After that, fill in the blanks on this chart with the following options: Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle, Electron Transport Chain, O2, H2O, Cytoplasm, Mitochondrial Matrix, and Inner membrane 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu 5.) Can you identify the role of energy rich intermediates and electron acceptors at different stages in respiration (glycolysis, Krebs cycle, Ox Phos)? ----- Finish the oxidation of these energy rich intermediates. Be sure to include the electrons and energy gain/release: i. NADH ii. FADH2 iii. ATP iv. GTP 6.) Can you illustrate the steps that lead to the ultimate production of ATP at the inner mitochondrial membrane? ----- Label the missing parts of the figure below. Find where the proton gradient is created and where the gradient is used to turn ADP into ATP: 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu Dr. Kukday’s “Can You?” Questions (Highlighted ones are addressed in this worksheet, you will need to address the ones that aren’t highlighted on your own time): Paralysis Case: 1.) Can you identify types of enzyme regulation (emphasis on feedback inhibition)? 2.) Can you predict the consequences of mutations in an enzyme that is part of a metabolic pathway? 3.) Can you compare aerobic and anaerobic respiration pathways with respect to differences in products and energy intermediates produced? 4.) Can you identify the role of energy rich intermediates and electron acceptors at different stages in respiration (glycolysis, Krebs cycle, Ox Phos)? 5.) Can you identify treatment options for PDCD based on knowledge of the reactions catalyzed by PDH and the aerobic respiration pathway as a whole? DNP Case: 1.) Can you illustrate the steps that lead to the ultimate production of ATP at the inner mitochondrial membrane? 2.) Can you identify or predict the effect of inhibitors of Ox Phos? 3.) Can you differentiate between the mechanism of action of these inhibitors of Ox Phos? (discussed in next class) 4.) Explain the connection between the effect of inhibition of Ox Phos with the symptoms that a person who consumes the inhibitors will experience? 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu