* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Modern Genetics - Hicksville Public Schools
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Life history theory wikipedia , lookup
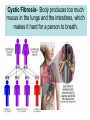
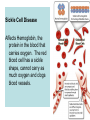
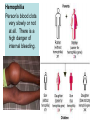
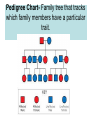
Human Inheritance- Important Facts 1) Sex chromosomes carry genes that determine whether a person is male or female. Girls have XX Boys have XY 2) Sex Linked genes- alleles are passed from parent to child on a sex chromosome. (Ex. Color blindness) 3) Carrier- Person who does not show a trait but can pass it on to their offspring. (They are hybrids for that trait) A person’s characteristics are determined by an interaction between genes and the environment. Human Genetic Disorders Some genetic disorders are caused by mutations in the DNA of genes. Other disorders are caused by changes in the structure or number or chromosomes. Cystic Fibrosis- Body produces too much mucus in the lungs and the intestines, which makes it hard for a person to breath. Sickle Cell Disease Affects Hemoglobin, the protein in the blood that carries oxygen. The red blood cell has a sickle shape, cannot carry as much oxygen and clogs blood vessels. Hemophilia Person’s blood clots very slowly or not at all. There is a high danger of internal bleeding. Down Syndrome A person’s cells have an extra copy of chromosome 21. People have some degree of mental retardation and heart defects are common. Pedigree Chart- Family tree that tracks which family members have a particular trait. 1. How many children did the original parents have? ____________ 2. What is the total number of children and grandchildren who are color-blind in this family? ___________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Branching Tree- shows how different organisms are related. Darwin’s Theory Darwin’s Observations • Diversity- He observed a variety of living things • Fossils- He observed fossils of animals that were no longer alive. • Galapagos Organisms- He observed that organisms in the Galapagos resembled those from mainland, but there were significant differences. Vocabulary • Adaptation- Trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce. Examples: beak shape for birds, a plant that tastes bad or is poisonous. • Evolution- Gradual change of a species over time. • Natural Selection- Process by which individuals that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. Over time, natural selection may lead to change. Helpful variations may accumulate while unfavorable ones may disappear. • Variation- Any difference between the organisms of the same species. • Competition- Organism compete with each other for food, mates and other resources. • Environmental change- A change in the environment can affect an organism's ability to survive which may lead to natural selection. Evidence of Evolution • Fossils • Patterns of early development • Similar body structures Advances in Genetics • Clone- organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it was produced. • Human Genome Project- Has the purpose to identify the DNA sequence of every gene in the human genome. • Selective Breeding- Process of selecting a few organisms with desired traits to serve as parents for the next generation.