* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bite Me!
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
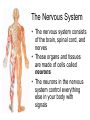
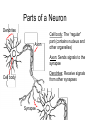
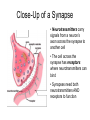
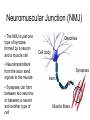
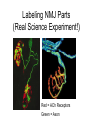
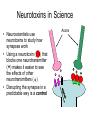
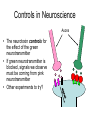
Bite Me! Neurons, synapses, and the venomous creatures that take advantage of them The Nervous System • The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves • These organs and tissues are made of cells called neurons • The neurons in the nervous system control everything else in your body with signals Parts of a Neuron Dendrites Axon Cell body: The “regular” part (contains nucleus and other organelles) Axon: Sends signals to the synapse Dendrites: Receive signals from other synapses Cell body Synapse Close-Up of a Synapse • Neurotransmitters carry signals from a neuron’s axon across the synapse to another cell • The cell across the synapse has receptors where neurotransmitters can bind • Synapses need both neurotransmitters AND receptors to function Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ) • The NMJ is just one type of synapse, formed by a neuron and a muscle cell • Neurotransmitters from the axon send signals to the muscle • Synapses can form between two neurons, or between a neuron and another type of cell Dendrites Cell body Synapses Axon Muscle fibers Acetylcholine (ACh) • ACh is one of many types of neurotransmitter • ACh is the neurotransmitter used at the NMJ • The unique structure of the ACh molecule allows it to fit in its receptor Close-Up of the NMJ • Neuron releases ACh from its axon • ACh crosses the synapse and binds to receptors in the muscle cell • Muscle responds to ACh signal by contracting NMJ In Real Life… • Where are the muscle fibers? Neurons? Synapses? • Where are the neurotransmitters? The receptors? Labeling NMJ Parts (Real Science Experiment!) Red = ACh Receptors Green = Axon Neurotoxins • Proper function of the nervous system is necessary for survival! • Molecules that interfere with the nervous system are called neurotoxins • Different neurotoxins can act on different parts of a synapse Neurotoxins in Nature • Neurotoxins occur naturally in some (not all) animal venoms • The animals pictured have neurotoxic venom • Neurotoxins in venom can disrupt the function of the NMJ Coral Snake Venom Venom Venom • Coral snake venom blocks ACh receptors • ACh cannot bind; no signals get through synapse • Muscle becomes paralyzed Black Widow Spider Venom • Black widow venom causes the axon’s ACh to be released all at once • No ACh left for intentional movement signals • The muscle spasms, then is paralyzed Neurotoxins in Science • Neuroscientists use neurotoxins to study how synapses work • Using a neurotoxin ( ) that blocks one neurotransmitter ( ) makes it easier to see the effects of other neurotransmitters ( ) • Disrupting the synapse in a predictable way is a control Axons Controls in Science Miracle-Gro Compost Ace Fertilizer Which kind of fertilizer is the best at making plants grow? Controls in Science Miracle-Gro CONTROL Ace Fertilizer Which kind of fertilizer is the best at making plants grow? Controls in Neuroscience Axons • The neurotoxin controls for the effect of the green neurotransmitter • If green neurotransmitter is blocked, signals we observe must be coming from pink neurotransmitter • Other experiments to try?