* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Goal 3 Guided Worksheet
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
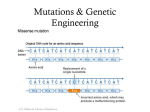
Name: ________________ Module 15 Lesson 3 Guided Notes Goal 3 I. DNA a. The structure of DNA is a ________________ or ________________ structure. b. The sides are composed of alternating ________________ groups. c. The “rungs of the DNA ladder” are composed of complementary ________________ always i. adenine, A to ___________________ ii. cytosine, C, to ___________________ iii. joined by weak ___________________. d. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA codes for ___________________, which is central key to cell function and life. e. Replication occurs during the ___________________ phase of the cell cycle and allows daughter cells to have an exact copy of parental DNA. f. Cells respond to their environments by producing different types and amounts of protein. g. With few exceptions, all cells of an organism have the___________________DNA but differ based on the___________________of genes. II. DNA a. Advantages of the overproduction of proteins at the incorrect times: __________________ b. Disadvantages of the overproduction, underproduction or production of proteins at the incorrect times: __________________ III. Protein Synthesis a. Process of protein synthesis: i. _____________________ that produces an RNA copy of DNA, which is further modified into the three types of RNA mRNA travels to the ribosome (rRNA) ii. _____________________ – tRNA supplies appropriate amino acids b. Amino acids are linked by _____________________ to form polypeptides. c. P_____________________ chains form protein molecules. d. Proteins can be _____________________ (forming a part of the cell materials) or _____________________ (hormones, enzymes, or chemicals involved in cell chemistry). e. An _____________________ _____________________ forms a protein that leads to a particular function and phenotype (trait) in an organism. IV. What amino acid corresponds with CCG on the chart? _____________________ V. Mutations a. Mutations are changes in DNA coding and can be _____________________, _____________________, _____________________ b. Mutations can be_____________________and spontaneous or caused by radiation and/or _____________________ c. Describe how mutations change amino acid sequence, protein function, phenotype. d. Only mutations in _____________________ (egg and sperm) or in the gamete produced from the primary sex cells can result in _____________________. VI. Meiosis a. Genes are on _____________ chromosome which allows them to be shuffled in meiosis. b. The process of meiosis leads to _______________ and ultimately to greater genetic diversity. c. Genetic variation in sexually reproducing organisms including i. ______________ ii. ______________________________________________ of chromosomes iii. _______________________________ iv. ___________________ failure of chromosomes to separate v. __________________: combination of 2 set of genes. VII. Random Assortment a. Meiosis is the cell division which takes place to form ________________ (sperm and egg cells). b. In the first metaphase the chromosomes line up in pairs along the____________________. c. The random assortment basically means they can line up in any order before they are pulled to either ends of the cell.... VIII. Mitosis Meiosis ____________Reproduction ___________ cell division 2 identical cells produced Makes ___________(somatic) cells Goes from diploid to _____________ Chromosome number stays the same. DNA is replicated. ______________ Reproduction Two cell divisions _______________ cells produced Makes ____________________ Goes from diploid to ___________ ( 2n to 1n) Chromosome number reduced. DNA is replicated IX. Genetics a. Determine parental genotypes based on offspring ratios. Example: B= brown, b= white If 3 out of the 4 offspring are Brown, what would the parents be? b. __________________________: Traits are equally expressed. Example: roan cow or blood types c. ____________________________: Blending of traits ; Example: four o’clock flower d. ______________________________ are controlled by more than one pair of genes and that this pattern of inheritance is identified by the presence of a wide range of phenotypes (skin, hair, and eye color). X. Karyotype XI. Punnett Square a. What is the genotypic(RR:Rr:rr) ratio of the square below?______________________ b. What is the phenotypic ( round: wrinkled) ratio? ________________________ XII. Genetics a. Autosomal inheritance patterns: i. Sickle cell anemia (incomplete dominance) 1. AA= normal but can get ______________ 2. Aa= c___________; doesn’t have the symptoms of sickle cell anemia and _________________get malaria. 3. aa= Has sickle cell anemia ii. Cystic fibrosis (recessive heredity) iii. Huntington’s disease (dominant heredity). XIII. Blood Types: Codominant and Multiple alleles Blood type Genotype A ______________ B B, B XIV. B I I I i AB ___________ O ______________ Sex- Linked Crosses a. Examples : ___________________ and hemophilia b. ____________________are more likely to express a sex-linked trait. c. Sex Linked traits are usually________________ and linked to the X chromosome. XV. Pedigrees a. Males: __________________ b. Females: ___________________ c. Affected: Shaded XVI. Environmental factors and genes a. lung/mouth cancer – tobacco use b. skin cancer – vitamin __________________, folic acid and sun exposure c. diabetes – diet/exercise and genetic interaction d. PKU – __________________ e. heart disease – diet/exercise and genetic interaction XVII. Gel Electrophoresis a. Use _________________ to cut DNA into different sized fragments b. Run those fragments on gels with l_____________ fragments moving slower than shorter ones. XVIII. Transgenic and Transformation a. Transgenic organisms (plants, animals, & bacteria) are used in agriculture and industry pharmaceutical applications such as the production of _____________________ b. The steps in bacterial transformation i. insertion of a ______________into a bacterial plasmid, ii. getting bacteria to take in the _____________________ iii. selecting the transformed bacteria iv. and producing the product XIX. Ethics a. Identify the reasons for establishing the Human Genome Project. i. Identify the __________________________ on a human’s chromosome. ii. The project is useful in determining whether individuals may carry genes for genetic conditions and in developing gene therapy. b. Gene therapy: Using ________________ to transfer the correct gene to a patient i. c. Used to treat: Severe Combined Immunodeficiency and Cystic Fibrosis Critique the ethical issues and implications of genomics and biotechnology (stem cell research, gene therapy and genetically modified organisms). XX. Evidence of Evolution a. Hypothesized early atmosphere and experiments that suggest how the first “cells” may have evolved and how early conditions affected the type of organism that developed Oparin’s hypothesis: ______________________; tested by Miller b. Steps of evolution i. first anaerobic and ___________________ ii. then photosynthetic iii. then eukaryotic iv. then ___________________ c. Fossil evidence informs our understanding of the evolution of species and what can be inferred from this evidence. i. _________________________ (molecular) similarities tell us what organisms have similar ancestors. ii. ________________________structures (homologies) tell us what organisms have similar ancestors. XXI. Natural selection a. Cause and effect model for the process of natural selection: i. Species have the potential to _______________________________________ ii. Populations are _________________________ due to mutations and genetic recombination. iii. There is a ____________________ supply of resources required for life. iv. Changing environments select for specific genetic phenotypes. v. Those organisms with____________________ adaptations survive, reproduce and pass on their alleles. vi. The accumulation and change in favored alleles leads to changes in species over time. b. Geographic isolation can cause _______________________. XXII. Resistance a. _______________________: transfer of immunity from one organism to another i. Mother to child ii. ______________: dead or live viruses injected into an animal iii. Body recognizes pathogens and is ready to kill it. b. Active immunity: A type of immunity or resistance developed in an organism by its own production of _______________________n response to an exposure to an antigen, a pathogen or to a vaccine. c. Antivirals and vaccines. XXIII. Classification a. Classification is constantly________________ based on new knowledge generated by research on evolutionary relationships and the history of classification system. b. Currently Seven levels: ______________________________________________________________________ c. Currently_____________ domains and_________ kingdoms: i. __________________, eubacteria, protist, fungi, plants, animals XXIV. Classification a. Dichotomous key: Always start with #________________ b. Phylogenetic tree : Used to find relationships and ______________________________________