* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Control of the cardiac cycle
Survey
Document related concepts
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
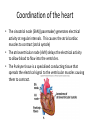
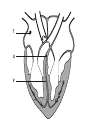
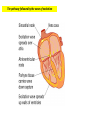
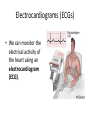
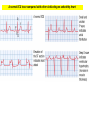
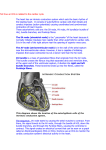
Control of the cardiac cycle Learning intentions • Describe how heart action is coordinated with reference to the sinoatrial node, the atrioventricular node and the purkyne tissue. • Interpret and explain electrocardiogram (ECG) traces with reference to normal and abnormal heart activity. What is Your Heart Rate? • Your pulse is the number of beats in 15 seconds then calculate for the number of beats per minute • Complete question 1 on the worksheet. The need for coordination • The heart of a mammal contains four main chambers. The action of these chambers is coordinated by electrical activity in specialised tissues that regulate the heart rate. Coordination of the heart • The sinoatrial node (SAN) (pacemaker) generates electrical activity at regular intervals. This causes the atrial cardiac muscles to contract (atrial systole) • The atrioventricular node (AVN) delays the electrical activity to allow blood to flow into the ventricles. • The Purkyne tissue is a specialised conducting tissue that spreads the electrical signal to the ventricular muscles causing them to contract. T U V The pathway followed by the wave of excitation Electrocardiograms (ECGs) • We can monitor the electrical activity of the heart using an electrocardiogram (ECG). Electrocardiogran (ECG) Electrodes are placed on the skin over opposite sides of the heart, and the electrical potentials generated recorded with time. The result is an ECG. P wave = electrical activity during atrial systole QRS complex = electrical activity during ventricular systole T wave = ventricular repolarisation (recovery of ventricular walls) Q-T interval – contraction time (ventricles contracting) T-P interval – filling time – ventricles relaxed and filling with blood A normal ECG trace compared with others indicating an unhealthy heart Activity • Students will answer questions on page 59 • Students will attempt some past paper questions.