* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Describe the cardiac conduction system and an ECG. Tell how an
Survey
Document related concepts
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
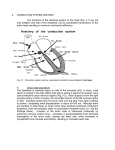
Tell how an ECG is related to the cardiac cycle. The heart has an intrinsic conduction system which sets the basic rhythm of the beating heart. It consists of autorhythmic cardiac cells that initiate and conduct impulses (action potentials) causing coordinated and synchronized contraction of heart muscle. These autorhythmic cells are: the SA node, AV node, AV bundle(or bundle of His), bundle branches, and Purkinje fibres. The SA node (sinoatrial node) is the" pacemaker" of the heart because it normally initiates impulses more rapidly than other autorhythmic cardiac cells. It is in the wall of the right atrium near the opening of superior vena cava. The AV node (atrioventricular node) is in the wall of the atrial septum near the atrioventricular valves. However, it too is capable of initiating impulses that cause contraction but at a slower rate than the SA node. AV bundle is a mass of specialized fibres that originate from the AV node. This bundle crosses the fibrous ring that separates atria and ventricles then, at the upper end of the ventricular septum, it divides into right and left bundle branches. These branches break up into fine fibres, called the Purkinje fibres. This diagram shows the location of the autorhythmic cells of the intrinsic conduction system. The sequence: AV node starts by causing the atrial muscles to contract. From there, the signal travels to the AV node, through the bundle of HIS, down the bundle branches, and through the Purkinje fibers, causing the ventricles to contract. This signal creates an electrical current that can be seen on a graph called an Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). Doctors use an ECG to monitor the cardiac conduction system’s electrical activity in the heart. The ECG The Electrocardiogram is a voltage difference, recorded between two electrodes on the surface of the body, usually on two limbs. The electrodes connect to the switch unit and then to a high-gain amplifier and isolation unit. The normal ECG tracing shows five waves which, by convention, have been named P,Q,R.S and T. The QRS complex: is due to ventricular depolarization, and it marks the beginning of ventricular systole. It is so large that it masks the underlying atrial repolarization signal. The T wave: is due to ventricular repolarization. The end of the T wave marks the end of ventricular systole electrically. In abnormal ECGs, the events generated by the atria and the ventricles might be uncoupled, such as in the absence of SA node activity or in the case of atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation. In cases in which the ventricles themselves behave abnormally, ..multifocal intraventricular extrasystoles or even fatal ventricular fibrillation is seen. 2- In what type of vessels is the blood pressure highest? Lowest? neficial? The highest blood pressure is in arteries (especially in aorta) while the lowest is in veins (especially in vena cava). The flow of blood in capillaries is very slow to allow for the exchange of gases and wastes.

















![Cardio Review 4 Quince [CAPT],Joan,Juliet](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008476689_1-582bb2f244943679cde904e2d5670e20-150x150.png)