* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Buddhism PPT - Montville.net
Buddhist influences on print technology wikipedia , lookup
Wat Phra Kaew wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and violence wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist cosmology of the Theravada school wikipedia , lookup
Triratna Buddhist Community wikipedia , lookup
Persecution of Buddhists wikipedia , lookup
Four Noble Truths wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist art wikipedia , lookup
Noble Eightfold Path wikipedia , lookup
Tara (Buddhism) wikipedia , lookup
Early Buddhist schools wikipedia , lookup
Pratītyasamutpāda wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist texts wikipedia , lookup
Gautama Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Buddha-nature wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Thailand wikipedia , lookup
Korean Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Chinese Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist ethics wikipedia , lookup
Dalit Buddhist movement wikipedia , lookup
Nirvana (Buddhism) wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and psychology wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist meditation wikipedia , lookup
Dhyāna in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Sanghyang Adi Buddha wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in Cambodia wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Japan wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Western philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
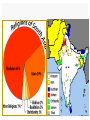
History of Buddhism in India wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Vietnam wikipedia , lookup
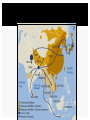
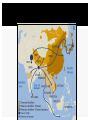
Silk Road transmission of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
Enlightenment in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
THE LIFE OF BUDDHA • Much of what is known about life of the Buddha from accounts in Buddhist literature • Gautama born 500s BC • Prince of small kingdom in what is now Nepal – Led sheltered life – Unaware of hardship – Life changed when learned people got old, sick, died BUDDHA’S ENLIGHTENMENT •Gautama resolved to find way to overcome age, sickness, keep people from suffering •Gave up possessions, left palace •Sought enlightenment, spiritual understanding for six years •Studied with gurus, monks but decided they could not teach way to enlightenment Sat under tree, no teachers, no companions, determined not to arise until he found way Stories say he meditated all night Resolve tested by violent storms, earthly temptations At daybreak, had been transformed, found enlightenment, became the Buddha, Enlightened One Temple built where he meditated, Bodh Gaya, one of Buddhism’s most sacred places THE FOUR NOBLE TRUTHS There is suffering in the world The cause of self suffering is self centered desire The solution is to eliminate desire and attachments To reach nirvana you must follow the Eightfold Path BELIEFS OF BUDDHISM A major change in Gautama’s thinking was when he decided to stop looking outwardly to understand the cause of suf fering. Instead, he decided to look within his own mind. Instead of worshipping gods or a god, Buddha taught his followers that the answer to human suf fering was in right thinking and self-denial. A big dif ference between Buddhism and other major religions is that in Buddhism you do not worship many gods or even one god. GIVING UP DESIRES According to Buddha, human suffering happens because of our selfish desires for things like power, wealth, and pleasure. The way to be happy was to give up those selfish desires. He called this path to happiness the Middle Way = MODERATION In Buddhism, people are to act unselfishly, treat people fairly, tell the truth all the time, avoid violence and the killing of any living thing When people learned to follow this Buddhist Middle Path, they would find lasting peace, called nir vana. Once a person reached this point, that person would no longer need to go through reincarnation THE EIGHTFOLD PATH SPREAD OF BUDDHISM Theravada Buddhism The oldest school of Buddhism. The “Way of the Elders” or the “Small Vehicle.” Found in southern Asia. The monastic life is the best way to achieve nirvana. Focus on wisdom and meditation. Goal is to become a “Buddha,” or “Enlightened One.” Over 100,000,000 followers today. Theravada Buddhism Mahayana Buddhism The “Great Vehicle.” Founded in northern Asia (China, Japan). Buddhism “for the masses.” Seek guidance from Boddhisatvas, wise beings. Goal: Not just individual escape from the wheel, but the salvation of all humanity through self-sacrifice of those enlightened few. Tibetan Buddhism The “Diamond Vehicle.” [Vajrayana] Developed in Tibet in the 7c CE. A mix of Theravada and Mahayana. Boddhisatvas include Lamas, like the Dalai Lama. The Tibetan Book of the Dead [Bardo Thodol]. Zen Buddhism The “Meditation School.” Seeks sudden enlightenment [satori] through meditation, arriving at emptiness [sunyata]. Use of meditation masters [Roshi]. Beauty, art, and aesthetics: Gardens. Archery. Tea ceremony. Calligraphy.