* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download aztecs - taughtbygoldin
Texcoco, State of Mexico wikipedia , lookup
Bernardino de Sahagún wikipedia , lookup
The Indian Emperour wikipedia , lookup
Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire wikipedia , lookup
Tepotzotlán wikipedia , lookup
Fall of Tenochtitlan wikipedia , lookup
National Palace (Mexico) wikipedia , lookup
Templo Mayor wikipedia , lookup
Aztec Empire wikipedia , lookup
Aztec warfare wikipedia , lookup
Human sacrifice in Aztec culture wikipedia , lookup
Aztec cuisine wikipedia , lookup
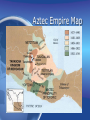
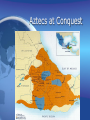
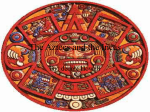
The Azteca I am Peter I eat Boogers Early 1200s-early 1500s aka Mexica History of the Aztec Nation The Aztecs are believed to have come from the north. They spoke the Nahuan, or Nahuatl, language. This tongue belongs to the Uto-Aztecan linguistic stock. It is related to the languages of the Piman and Shoshonean tribes of the western United States mexico Mexico • The emblem-shield symbolizes the Aztec heritage. • According to a beautiful legend, the gods had advised the Aztecs that the place where they should establish their city was to be identified when they saw an eagle, perched on a prickly pear tree, devouring a serpent. They saw this mythical eagle on a marshy lake that is now the zócalo or main plaza in Mexico City. Lake Texococo. Aztec Empire Map Aztecs at Conquest Warriors at Play Sons of Dogs-Chichemecas • Azitlan-S. of Mazatlan on coast, possible origin point. • They have really old chinampas Nomadic Farmers • Their legends reveal the early Aztecs as a nomadic farming people, wandering about in search of fertile land. In the Valley of Mexico, they fought with the settled tribes and at times were forced to serve them. Eventually, they forced others to serve them. What did they eat? • Finally they took refuge on islands in the shallow lakes and founded Tenochtitlán on the site of modern Mexico City in about 1325. Prosperous? • Here they prospered and reached out to win new lands. They allied themselves with other Nahua tribes. Soon the Tenocha Aztecs dominated the Aztec Confederacy. They were at the height of their power when the Spaniards attacked them. The Indians living in the Mexico City region today are largely descendants of those whom Cortez conquered. Civilized Barbarians • The Aztecs had the most advanced civilization in North America at the time of Cortez, but they did not originate it. When they invaded the region, they took over the culture of earlier, more advanced peoples— the Toltecs, Mayas, Zapotecs, and others. The barbarian Aztecs came to Mexico in about AD 1200 religion • Religion was the great controlling force in Aztec life. In architecture and sculpture they gave their best efforts to building and decorating huge temples. They had picture writing, hieroglyphics, and number symbols with which they recorded religious events and historic annals. Aztec Temple Astronomy • They had learned from the Mayas how to determine the solar year accurately. . . . With this knowledge their priests kept an exact solar calendar. An almanac gave dates for fixed and movable festivals and listed the various deities who held sway over each day and hour. Aztec Calendar Trade • A trade system linked the far parts of the empire with Tenochtitlán. Soldiers guarded the traders, and troops of porters carried the heavy loads, for the Aztecs had no pack animals. Canoes brought the crops from nearby farms through the canals to markets in Tenochtitlán. • Their chief produce included corn, beans, peppers, squash, alligator pears, tomatoes, tobacco, cotton, and turkeys. Trade was carried on by barter, since the Aztecs had not invented money. Change could be made in cacao beans. Life in the Capital • The Aztecs used their wealth and power to provide a brilliant life in their capital. Montezuma lived in a splendid palace. He was surrounded by his nobles and served by thousands of slaves. In the palace grounds were beautiful gardens and menageries. Read article on Tenochititlan. Tenchititlan by Europeans El Chapultapec • The city streets and palace walls were scrubbed dazzlingly white by sweating slaves. Bridges carried the streets over the network of canals which laced the city. An aqueduct brought drinking water from Chapultepec, a rocky height nearby Chapultapec castle today Chinampas • Strange floating islands fringed the oval main island. They were made of mud dredged up from the lake bottom, supported on a network of branches and water grass. At first, the farmers could tow them with canoes. Then, as trees sent down roots, they became permanent island farms, called chinampas Chinampas-then and now Mud Huts • Farmers lived in wattle-and-daub huts on these islands. In the older sections of the city officials lived in houses of stone and adobe. Each house was built around a patio and raised on a platform for protection against lake floods. Most Aztecs were farmers. There were also traders and craftsmen. Aztec Family Life • Custom governed many details of child rearing—even the number of tortillas to be fed at various ages. Children were taught courtesy, respect for their elders, truthfulness, and self-control. Boys Life • Aztec boys learned practical tasks from their fathers at home, then went to the house of youth (called telpuchcalli) at the age of 15. Here older men of each clan taught the boys the duties of citizenship, religious observances, the history and traditions of their people, and arts and crafts. Training for war included learning to use the javelin thrower (called the atlatl), bows and arrows, and wooden war clubs with sharp blades of obsidian. In another school, the calmecac, boys studied for the priesthood. Girls could learn to be priestesses in temple schools. Tribal Organization • Aztec tribes were divided into families and clans. Each clan had its own elected officials and sent representatives to the council of the tribe. The council appointed officials to govern the four quarters (phratries) in which the city was organized. The council also elected and advised the supreme chief, who led the tribe in wars and alliances. A second chief supervised internal affairs. Tribal organization(continued) • Although the system was theoretically democratic, actually the chiefs were selected from powerful families. It was theocratic rule. The priesthood had a strong influence in tribal affairs but probably took no active part in government. Strict laws and courts protected common citizens and even slaves from many forms of injustice. Crimes and disorder were severely suppressed. Theft of growing corn was punished by slavery or execution Land Ownership • Land was held in common by the tribes. The council apportioned shares to heads of families. They controlled the land, however, only as long as it was cultivated. Sections were also farmed to provide food for chiefs and priests. Everybody paid tribute to the Emperor. He liked payment in goods and girls. The Gods • The Aztecs worshiped a host of gods who personified the forces of nature. To obtain the gods' aid, the worshipers performed penances and took part in innumerable elaborate rituals and ceremonies. Human sacrifice played an important part in the rites. Since life was man's most precious possession, the Aztecs reasoned, it was the most acceptable gift for the gods. As the Aztec nation grew powerful, more and more sacrifices were needed to keep the favor of the gods. At the dedication of the great pyramid temple in Tenochtitlán, 20,000 captives were killed. They were led up the steps of the high pyramid to the altar, where chiefs and priests took turns at slitting open their bodies and tearing out their hearts. Aztec Warrior Fine Young Cannibals • The Aztecs sometimes practiced cannibalism; that is, they ate the flesh of their victims, believing that they would then absorb the virtues of the slain. The sacrificed victims were thought to win a high place in paradise. The need for collecting captives led Aztec warriors to seek prisoners instead of killing their enemies in battle. Spaniards Freaked Out at This • The Spaniards were horrified by these Aztec rites, and after the conquest they ruthlessly destroyed the temples in order to blot out the old faith. The friars who came to convert the Indians to Christianity and to educate them added to the destruction by burning records and shattering idols. They frequently built a Christian church on the rubble left when the old temple was torn down. Hernan Cortez in D.F. Cortez • Cortez lived for a time in the temple area- he had crosses and virgin Mary statutes erected over paganistic symbols and cleaned up the bloody mess. They forced the Aztecs to worship Mary and Jesus.