* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Processes
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
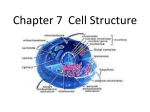
Cell Processes Name: __________________________________________________________ Read about the various processes that cells do for you, non-stop, 24/7 to keep you alive (see reverse side of this assignments). Then read each of the 20 statements below and write down the matching cell process. The 9 processes are listed below in a word bank for reference. NUTRITION DIGESTION ABSORPTION BIOSYNTHESIS RESPIRATION EXCRETION SECRETION REPRODUCTION RESPONSE _________________ 1. An organism grows in size. _________________ 2. Hormones are produced by glands in the body _________________ 3. The removal of wastes from the body. _________________ 4. Complex food particles are broken down to simpler forms _________________ 5. A small fracture in your bone heals. _________________ 6. 6CO2 + 6H2O LIGHT & CHLOROPHYLL C6H12O6 + 6O2 _________________ 7. Energy is released from the combination of glucose and oxygen. _________________ 8. A plant bends toward sunlight. _________________ 9. A frog lays eggs. _________________ 10. Food molecules pass into the cell. _________________ 11. Hemoglobin (what makes blood red) is manufactured by the cell. _________________ 12. A muscular contraction. _________________ 13. Insulin, growth hormone, adrenalin, testosterone, estrogen, sweat _________________ 14. Carbohydrates, lipids (i.e. fats) and proteins satisfy this need _________________ 15. Proteins are broken down into individual parts called amino acids. _________________ 16. C6H12O6 + 6O2 MITOCHONDRIA 6CO2 + 6H2O + (36 ATP) _________________ 17. The end result of mitosis (you may have to look this word up) _________________ 18. The roots of a plant grow toward water. _________________ 19. You eat lunch in the cafeteria. _________________ 20. You become ill when a test is announced. Chapter 4: The Structure and Function of Cells : Important Summary Concepts 1. The cell theory states that: • every living thing is made of cells, • cells are the units of structure and function for all living things • cells must come from pre-existing cells. 2. All the processes of a living cell involve energy transformations provided by chemical activity within the cell. The cell processes are nutrition, digestion, absorption, synthesis, respiration, excretion, secretion, movement, response, and reproduction. 3. The nucleus is the control center of cellular activities. DNA is the “boss” of the cell and is passed down from one generation to another. PROKARYOTIC cells such as bacteria have no nucleus but still possess DNA to direct cellular functions. EUKARYOTIC cells have a nucleus which housed the DNA. EUKARYOTIC cells also have ORGANELLES (individual structures that carry out specific functions within the cell) 4. Cytoplasm contains various individual structures called organelles. Each organelle is associated with a specific activity within the cell. The organelles function together like the different instruments in a symphony. They must all work at the same time for the cell to function at all. 5. The chlorophyll-containing chloroplasts of a green plant cell allow the cell to make food from inorganic compounds, i.e. PHOTOSYNTHESIS. This puts plants in an important biological position. 6. Plant cells are enclosed in a rigid cell wall which is not present in animal cells. 7. The organization of living things can be considered on various levels: • Organisms can be just one cell big, like bacteria or pond water critters. • Organisms like plants, animals and fungi (EUKARYOTES) are more complex and follow a hierarchy: CELL…TISSUE…ORGAN…ORGAN SYSTEMS…ORGANISM. • More levels leads to more specialized functions. Multicellular organisms are like a symphony where each section of the orchestra plays a specific role. When even one instrument is out of tune, it effects the whole performance.