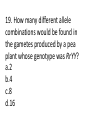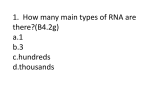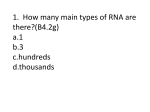* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EXAM Banswers2 - HonorsBiologyWiki
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
1. How many main types of RNA are there?(B4.2g) a.1 b.3 c.hundreds d.thousands 2.Which type(s) of RNA is(are) involved in protein synthesis?(B4.2g) a.transfer RNA only b.messenger RNA only c.ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA only d.messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA 3.What amino acid is coded with GAU? Use Figure 12-2 show? (B4.2f) a.Cys b.Stop c.Met d.Asp 4. During transcription, an RNA molecule is formed(B 4.2g) A.that is complementary to both strands of DNA. B.that is identical to part of a single strand of DNA. C.that is double-stranded. D.inside the nucleus. 5. Why is it possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon A.Some codons have the same sequence of nucleotides. B.There are 64 different kinds of codons but only 20 amino acids. C.Some codons do not specify an amino acid. D.The codon AUG codes for the amino acid methionine and serves as the “start” codon for protein synthesis. 6. What happens during the process of translation? A.Messenger RNA is made from DNA. B.The cell uses information from messenger RNA to produce proteins. C.Transfer RNA is made from messenger RNA. D.Copies of DNA molecules are made. 7. Genes contain instructions for assembling A.purines. B.nucleosomes. C.proteins. D.pyrimidines. 8. A mutation that involves a single nucleotide is called a(an) A.chromosomal mutation. B.inversion. C.point mutation. D.translocation. 9. Which of the following is NEVER a frameshift mutation? a.substitution b.insertion c.deletion d.inversion 10. Consider the cell labeled X in Figure 109 containing 4 chromosomes. Which of the four cells below it represents a healthy gamete that could be produced from this cell? a.A b.B c.C d.D 11. Gametes have a.homologous chromosomes. b.twice the number of chromosomes found in body cells. c.two sets of chromosomes. d.one allele for each gene. 12. During which phase of meiosis do homologous pairs of chromosomes line up next to one another along the equator? a.anaphase I b.metaphase I c.prophase II d.metaphase II 13. Gametes are produced by the process of a.mitosis. B.meiosis. C.crossing-over. D.replication. 14. The numbers in Figure 10-1 represent the chromosome number found in each of the dog cells shown. The processes that are occurring at A and B are ____. A.mitosis and fertilization B.meiosis and fertilization C.mitosis and pollination D.meiosis and pollination 15. Chromosome number is reduced by meiosis because between meiosis I and meiosis II A. crossing-over occurs. B. metaphase occurs. C. replication occurs twice. D. replication does not occur. 16. Mendel’s principles of genetics apply to A.plants only. B.animals only. C.pea plants only. D.all organisms. 18. Offspring that result from crosses between true-breeding parents with different traits A. are true-breeding. B. make up the F2 generation. C. make up the parental generation. D. are called hybrids. 19. If a pea plant has a recessive allele for green peas, it will produce … A.green peas if it also has a dominant allele for yellow peas. B.both green peas and yellow peas if it also has a dominant allele for yellow peas. C.green peas if it does not also have a dominant allele for yellow peas. D.yellow peas if it does not also have a dominant allele for green peas. 19. How many different allele combinations would be found in the gametes produced by a pea plant whose genotype was RrYY? a.2 b.4 c.8 d.16 20. Situations in which one allele for a gene is not completely dominant over another allele for that gene are called A.multiple alleles. B.incomplete dominance. C.dominant inheritance. D.multiple genes. 21. A cross of a red cow with a white bull produces all roan (a combination of both red and white hair) offspring. This type of inheritance is known as A.incomplete dominance. B.polygenic inheritance. C.codominance. D.multiple alleles. 22. What principle states that during gamete formation genes for different traits separate without influencing each other’s inheritance? (B4.1d) a.principle of dominance b.principle of independent assortment c.principle of probabilities d.principle of segregation 23. The failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis is called A.nondisjunction. B.X-chromosome inactivation. C.Turner’s syndrome. D.Down syndrome. 24. Human females produce egg cells that have A.one X chromosome. B.two X chromosomes. C.one X or one Y chromosome. D.one X and one Y chromosome. 25. Which of the following genotypes result in the same phenotype?) A.AA and AB b.BB and BO c.BB and AB d.BOand OO 26. A DNA molecule containing regions from different sources is called A.DNA ligase. B.recombinant DNA. C.restriction DNA. D.template DNA. 27. Which outcome is possible using genetic engineering, but not using selective breeding? A.A sheep with wool longer than wool produced by any other sheep. B.Corn that produces one large corn cob per plant. C.A bacterium that produces human insulin. D.A hairless variety of cow. 28. The purpose of gene therapy is to A.cure genetic disorders. B.determine the sequences of genes. C.remove mutations from genes. D.change dominant alleles to recessive alleles. The pelvis and femur of the whale shown in Figure 15-2 A.allow the whale to walk. B.are vestigial structures. C.are acquired traits. D.are not inherited. 30. Common cells growing in similar patterns in different organisms produce A.homologous structures such as wings and arms. B.indistinguishable early embryos. C.vestigial organs such as reduced tails. D.different limb types specialized for a single function. 31. What is true about gene pools? A.They typically contain two or more alleles for each inheritable trait. B.They contain primarily dominant alleles. C.They contain primarily recessive alleles. D.The relative frequencies of alleles in gene pools are changed by sexual reproduction. 32. Genetic engineering involves A.reading a DNA sequence. B.editing a DNA sequence. C.reinserting DNA into living organisms. D.all of the above Individuals at only one end of a curve of phenotypic frequencies have higher fitness A. Directional Selection B. Stabilizing Selection C. Disruptive Selection D. Genetic Drift 34. Natural selection acts directly on A.alleles. B.genes. C.phenotypes. D.mutations. 35. The result of genetic drift that follows the colonization of a new habitat by a few individuals is called A.the Hardy-Weinberg principle. B.the founder effect. C.selection on single-gene traits. D.selection on polygenic traits. 36. Genetic drift tends to occur A.in very large populations. B.in small populations. C.only in new species. D.following stabilizing selection. 37. An analysis of derived characters is used to generate a a.family tree based on only external appearance. B.family tree based on only DNA structure. C.cladogram. D.traditional classification system. 39. The process by which organ systems maintain a controlled, stable, internal environment is called A.circulation. B.organization. C.homeostasis. D.teamwork. 39 An immune response is triggered by a(an) (B2.6a) A.antibiotic. B.antibody. C.antigen. D.histamine. 40. Homologies are similarities of structure that indicate A.common physical characteristics. B.diversity. C.related ancestry. D.similar biochemistry. 41. Cytoplasmic inheritance refers to A.genetics of certain organelles. B.the reproduction of chromosomes in the nucleus. C.paternal inheritance. D.introns. 42. This process noticeably begins at the gastrula stage. a.cell division b.cell differentiation c.cell fertilization d.cell activation 43. Barbara McClintock’s observations of streaking in corn plants led to her theory of A.imprinting. B.Zea mays. C.transposable elements. D.repression. 44. Proteins are an excellent mechanism by which genetic information is expressed because unlike sugars, lipids, and nucleotides, proteins A.can be metabolized to make energy that will be used throughout the body. B.can be structural or catalytic molecules or may be involved in cell-cell communication. C.are easily transported in the body. D.can replicate themselves. 45. What happens during gamete formation? A.a change from diploid to haploid B.a change from haploid to diploid C.no change in chromosome number