* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.B.1 Conserved Core Processes
Survey
Document related concepts
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
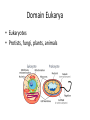
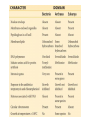
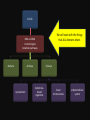
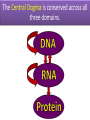
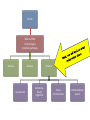
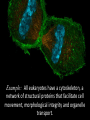
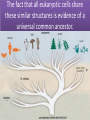
1.B.1 Conserved Core Processes Organisms share many conserved core processes and features that evolved and are widely distributed among organisms today. Structural and functional evidence supports the relatedness of all domains. Domain Bacteria • Prokaryotes • No membrane-bound organelles or nuclei • Peptidoglycan in cell walls • Rapid reproduction and mutation • May want to review Ch 27 Domain Archaea • Prokaryotes • Share certain traits with bacteria and others with eukaryotes • …but also have own unique characteristics • Many are extremophiles (“lovers of extreme conditions”) Domain Eukarya • Eukaryotes • Protists, fungi, plants, animals Eukaryotic Kingdoms Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Number of cells Unicellular to multicellular Unicellular to multicellular Multicellular Multicellular How it obtains energy Autotroph or heterotroph Heterotroph Autotroph Heterotroph Cell wall? Generally, no (but some do) Yes (made of chitin) Yes (made of cellulose) No Example Volvox, Paramecium, Euglena Mushrooms, yeast, molds Ferns, trees, flowers Worms, dogs, humans The following core processes provide evidence that all organisms (both extant and extinct) are linked by lines of descent from common ancestry. All Life We will start with the things that ALL domains share. DNA and RNA Central Dogma metabolic pathways Bacteria Archaea cytoskeleton Eukarya membranebound organelles linear chromosomes endomembrane system DNA and RNA are the carriers of genetic information for all domains of life. The Central Dogma is conserved across all three domains. The genetic code is universal and shared by all modern organisms. Metabolic pathways are conserved across all domains. All Life DNA and RNA Central Dogma metabolic pathways Bacteria Archaea cytoskeleton Eukarya membranebound organelles linear chromosomes endomembrane system Structural evidence supports the relatedness of all eukaryotes. Example: All eukaryotes have a cytoskeleton, a network of structural proteins that facilitate cell movement, morphological integrity and organelle transport. Example: All eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts Example: All eukaryotes have linear chromosomes Example: All eukaryotes have endomembrane systems, which includes the nuclear envelope, the ER, the Golgi apparatus, and vesicles. Hint: this would be a great time to review the endomembrane system and what it does! Here is a simple animation for you: http://goo.gl/rhY8Xs The fact that all eukaryotic cells share these similar structures is evidence of a universal common ancestor.