* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download S3-Wheeler.pps
Numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
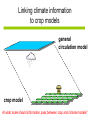
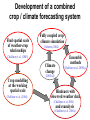
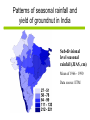
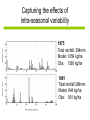
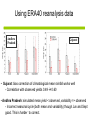
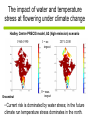
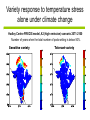
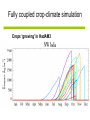
Development of a combined crop and climate forecasting system Tim Wheeler and Andrew Challinor [email protected] Crops and Climate Group A combined crop and climate forecasting system Report from: ‘Food Crops in a Changing Climate’ Linking climate information to crop models general circulation model crop model At what scale should information pass between crop and climate models? Development of a combined crop / climate forecasting system Find spatial scale of weather-crop relationships Fully coupled cropclimate simulation Osborne (2004) Challinor et. al. (2003) Climate change Crop modelling at the working spatial scale Challinor et. al. (2004) Ensemble methods (Challinor et al, 2005b,c) (2005c,d) Hindcasts with observed weather data (Challinor et al, 2004) and reanalysis (Challinor et al, 2005a) Simple correlations between rainfall and crop yield Seasonal rainfall and groundnut yields for all India. Time trend removed. rainfall yield Patterns of seasonal rainfall and yield of groundnut in India District level groundnut yields (kg ha-1) Mean of 1966 - 1990 Data source: ICRISAT Patterns of seasonal rainfall and yield of groundnut in India Sub-divisional level seasonal rainfall (JJAS, cm) Mean of 1966 - 1990 Data source: IITM General Large Area Model for Annual Crops (GLAM) • Aims to combine: – the benefits of more empirical approaches (low input data requirements, validity over large spatial scales) with – the benefits of a process-based approach (e.g. the potential to capture intra-seasonal variability, and so cope with changing climates) • Uses a Yield Gap Parameter to account for the impact of differing nutrient levels, pests, diseases, non-optimal management to simulate farm yields Challinor et. al. (2004) Hindcasts of groundnut yield for all India using GLAM -1 ) 1200 National Yield Statistics 1100 Groundnut yield (kg ha 1000 GLAM simulation 900 800 700 600 500 400 1965 1970 1975 1980 Year 1985 1990 Capturing the effects of intra-seasonal variability 1975 Total rainfall: 394mm Model: 1059 kg/ha Obs: 1360 kg/ha 1981 Total rainfall 389mm Model: 844 kg/ha Obs: 901 kg/ha Using ERA40 reanalysis data Andhra Pradesh Gujarat • Gujarat: bias correction of climatological mean rainfall works well - Correlation with observed yields 0.49 0.60 • Andhra Pradesh: simulated mean yield < observed, variability >> observed - Incorrect seasonal cycle (both mean and variability) though Jun and Sept good. This is harder to correct. Using probabilistic climate forecasts Model average 63 ensemble members 25 713 kg ha-1 775 kg ha-1 Frequency Observed 20 15 10 5 0 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 Yield (kg ha-1) Use of DEMETER multi-model ensemble for groundnut yield in Gujarat, 1998 from Challinor et al (2005) Probabilistic forecasting of crop failure • The number of ensemble members predicting yield below a given threshold is an indication of probability of occurrence • Found predictability in crop failure The impact of water and temperature stress at flowering under climate change Hadley Centre PRECIS model, A2 (high emission) scenario 1960-1990 Groundnut 1 = no impact 2071-2100 0 = max. impact • Current risk is dominated by water stress; in the future climate run temperature stress dominates in the north. Variety response to temperature stress alone under climate change Hadley Centre PRECIS model, A2 (high emission) scenario 2071-2100 Number of years when the total number of pods setting is below 50%. Sensitive variety Tolerant variety An integrated approach to climate impact assessments • Crops can modify their own environment – The water cycle and surface temperatures vary according to land use • Integrate biological and physical modelling – By working on common spatial scale – By fully coupling the models Fully coupled crop-climate simulation Crops ‘growing’ in HadAM3 Fully coupled crop-climate simulation All-India groundnut yield (red) with simulated mean yield (black) and spatial standard deviation (grey shading). Using satellite estimates of rainfall TAMSAT Teo Chee-Kiat David Grimes Conclusions • A combined crop and climate modelling system has been developed and tested for the current climate. – It shows skill in seasonal hindcasts and with climate ensembles – It has been used to study crop responses to climate change – Can be fully coupled to a GCM, and driven by satellite data