* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Non-coding RNAs are widely distributed in the 3 life domains
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
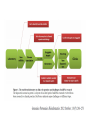
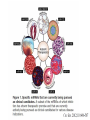
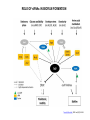
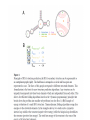
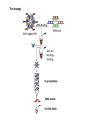
RNOMICS J. H. Leitão March 2017 Non-coding RNAs are widely distributed in the 3 life domains ncRNA in Eukaryotes and RNAi Potential applications of miRNA in plants Bacterial sRNAs sRNA encoding Region Intergenig Region Lacks obvious start and stop codons ROLE OF sRNAs IN BIOFILM FORMATION Trends Microbiol. 2013 Jan;21(1):39-49. CsrA and CsrA homolog RsmA and effect of sequestration by sRNA(A) Gene expression is controlled by CsrA binding to leader segments of target mRNAs (e.g. pgaABCD involved in PGA biosynthesis and export) affecting their translation and stability. CsrA activity is repressed via sequestration of CsrA by sRNAs CsrB/C, thereby inhibiting CsrA regulatory activity. (B) CsrA activity is enhanced by CsrD as well as the sRNA McaS, a component of the CsgD network which represses CsgD. Repression by CsrA on pga mRNA translation is negated by NhaR, an activator of PGA biosynthesis. (C) Schematic overview of the signaling cascade that converges on the sRNAs RsmY and RsmZ, which act by sequestering the translational repressor RsmA. RsmA reciprocally regulates factors involved in the planktonic/sessile switch indicated by activation of genes involved in motility or by repressing genes required for biofilm formation (Pel, Psl polysaccharides). Dashed lines indicate that the connection has not been fully demonstrated or is not understood at the molecular level. Trends Microbiol. 2013 Jan;21(1):39-49. sRNAs from bacteria modes of action Identification and characterization of ncRNAs The miRNA database The Rfam database The Vienna package webserver Identification of Hfq-like proteins from bacteria of the Burkholderia cepacia complex The strategy