* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Security - The University of Texas at Dallas
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Cross-site scripting wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Security printing wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Authentication wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Electronic authentication wikipedia , lookup
History of cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Web of trust wikipedia , lookup
Social engineering (security) wikipedia , lookup
Cybercrime countermeasures wikipedia , lookup
Rainbow table wikipedia , lookup
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Certificate authority wikipedia , lookup
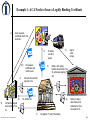
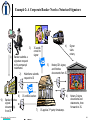
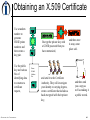
iSecuritas, Inc. secure authenticated data exchange Internet Security UTD EMBA March 30, 2001 iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 1 Who were the first “hackers”? • MIT's Tech Model Railroad Club • PDP - 1 • 1961 iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 2 You know your co-worker is a hacker when... • Everyone who ticks him or her off gets a $26,000 phone bill • Has won the Publisher's Clearing House Sweepstakes three years running • Massive 401k contribution made in half-cent increments • You hear them murmur, "Let's see you use that VISA card now, Professor "I-Don't-Give-A's-To Any MBA Candidate!" iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 3 How Secure is e-Business? •Security attacks cost U.S. corporations $266 million last year. That's more than double the average annual losses over the past three years. •Cyber-crimes being investigated by the FBI have more than doubled in the past year. • In 1999, the number soared to over 8,300 according to reports filed with the Computer Emergency Response Team, or CERT, at Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh. •90 percent of survey respondents (primarily large corporations and government agencies) detected some form of security breach last year. •70 percent of respondents reported a serious security breach in the past year (ie: financial fraud, denial of service attacks and data theft). According to a report recently released by the Computer Security Institute and the FBI Computer Intrusion Squad. iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 4 Categories of Internet Security • Website Security • Email Security • Authentication iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 5 All Systems are Breakable! iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 6 Website Security • Prevent Unauthorized Access to Website – Manipulation of Website Information – Protection of Proprietary Data • Credit Card Numbers • Confidential Customer Data • Financial Information iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 7 Website Security Website Security can be achieved by: • Firewalls • Software & System Architecture • Security Procedures iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 8 In God We Trust…. All Others We Monitor iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 9 Email Security Case Studies: • International Satellite Company • International Restaurant Company • Your Company? iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 10 Email Security Email Security can be achieved with: • Encryption Software – PGP, RSA, etc. • ASP Based Secure Messaging – iSecuritas iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 11 Authentication iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 12 Authentication iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 13 E-Sign Law New Law for E-Signatures • Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act • Effective October 1, 2000 • Nationwide Legality of Digital Signatures • Agnostic about Implementation of e-Signatures • Electronic Notarizations • Opportunity to marry e-commerce with official, regulated way for confirming identity • Reduces Fraud possible with Paper Based Notaries iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 14 Authentication Problem – Identity Theft • Fastest Growing Financial Crime » Industry Standard – August 21, 2000 • Theft of: • Social Security Numbers • Drivers License Numbers • Mothers’ Maiden Names • $1 Billion Problem? iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 15 Authentication Problem – Identity Theft Abraham Abdallah “a pudgy, convicted swindler and high school dropout”, NY Post March 20, 2001 Nyquist vs. E*Trade [Buckman, "Heavy Losses: The Rise and Collapse of a Day Trader," Wall Street Journal, Feb. 28, 2000] iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 16 Authentication Solutions (?) • Credit Card Transactions • Digital Certificates • Authentication Services iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 17 iSecuritas & MBE iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 18 iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential Example 1: A CA Needs to Issue a Legally Binding Certificate 1) User requests certificate from CA’s web site. 3) 10) 2) 8) 9) CA releases certificate and notifies user. IS sends e-mail to signer. 5) CA web site submits request to IS. IS notifies CA. 6) 7) Signer visits notary. Notary ID’s signer, fetches documents from IS, witnesses signing act. CA fetches signed document(s) from IS. iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 4) Notary D-signs documents and statements, then forwards to IS. IS applies 3rd party timestamp. 20 Example 2: A Corporate Banker Needs a Notarized Signature 3) 1) Banker submits a signature request to his company’s mainframe. 2) 8) 9) Banker fetches signed document(s) from IS. iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 4) IS sends e-mail to signer 5) Mainframe submits request to IS Notary ID’s signer, and fetches documents from IS IS notifies banker. 7) Signer visits notary 6) IS applies 3rd party timestamp. Notary D-signs documents and statements, then forwards to IS. 21 Example 3: A Distributor Needs a Digital Signature on a PO 1) 9) Signed PO sent to account rep , billing, shipping, etc.. 2) Distributor fetches signed PO from IS. iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential 4) 3) IS sends e-mail to signer. User fetches PO. 5) User fills out and D-Signs PO with notarized certificate, sends signed PO to IS. Web site submits request to IS. 7) 8) User requests PO on distributor’s web site. IS notifies Distributor. 6) IS applies 3rd party timestamp. 22 Encrypting with X.509 Bank wants to send Lawyer a secret message, but must do so on the public internet. Lawyer gives Bank their certificate. But Lawyer uses the gibberish iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential Bank verifies the certificate with the CA. And their private key Bank uses the public key from and a secret Lawyer’s message to certificate, Lawyer, As input to a decryption engine as input to an encrypti on engine, to produce what looks like gibberish To find out what Bank had to say 23 Signing with X.509 Lawyer wants proof that Bank wrote the message. as input to a Bank uses their hash engine gibberish to produce a hash,(signature) and their and uses this hash private key as input to an encryption engine and adds the encrypted hash to their gibberish. to produce a hash. Lawyer uses the as input to a hash engine gibberish (not the hash) iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential Then Lawyer takes Bank’s encrypted hash and Bank’s public key as input to a decryption engine to produce a hash. If both hashes match, then Lawyer knows that Bank signed the message. 24 X.509 Receipt Bank wants proof that Lawyer saw the message on the Internet, Lawyer must prove it. Lawyer uses as input to a hash Bank’s engine message Bank uses the signature and Lawyer’s public key iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential to produce a hash, and uses and this hash private key to produce a hash. as input to a decryption engine as input to an encryption engine Bank uses his original message To produce an encrypted hash (signature) as input to a hash engine to produce a hash, if the hashes match, we have a valid signature. 25 Obtaining an X.509 Certificate Use a random number to generate HUGE prime numbers and then create a key pair. Use the public key and various bits of identifying data to construct a certificate request, iSecuritas, Inc. Confidential Encrypt the private key with a GOOD password that you have memorized, Name E-Mail Address Etc. and send it to the Certificate Authority. They will investigate your identity to varying degrees, create a certificate that includes a hash encrypted with their private key, and then store it away some place safe. and then send you a copy as well as making it a public record. 26