* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alcohol - Staff Web Pages
Survey
Document related concepts
Disease theory of alcoholism wikipedia , lookup
Health effects of wine wikipedia , lookup
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Drug rehabilitation wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol and cancer wikipedia , lookup
Alcoholism in family systems wikipedia , lookup
Long-term effects of alcohol consumption wikipedia , lookup
Effects of alcohol on memory wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol abuse wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol and health wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
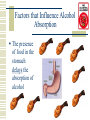
Alcohol Drug Unit S.O.L’s 9.1The student will apply health knowledge and skills to the development and analysis of personal goals to achieve and maintain long-term health and wellness. Key concepts/skills include c) development of personal standards regarding the use of alcohol, tobacco, and other harmful substances; f) establishment of personal parameters for appropriate and inappropriate health behaviors; 9.3The student will analyze, synthesize, and evaluate the relationships among positive health behaviors, prevention and treatment of injury, and premature death. Key concepts/skills include c) identification of situations involving risks; e) the effects of alcohol and other drug use. Drug Unit S.O.L’s 9.4The student will use various sources of information to evaluate global health issues. Key concepts/skills include b) the benefits of information provided by recognized sources, such as state and local health departments, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the American Dietetic Association (ADA), the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the World Health Organization (WHO), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 9.5 The student will evaluate the benefits of collaboration in relation to community health and wellness initiatives. Key concepts/skills include a) the impact of developing positive relationships among health, wellness, and safety professionals for promotion of healthy communities; c) development of school and community health programs for citizens of all ages; d) the need for community services; e) the awareness of health-related social issues such as organ donation, homelessness, underage drinking, and substance abuse. Bell Ringer #3 Write a half a page red to red on one of the below statements. Save these to be turn in on test day. Worth 10 points. 1. Do you agree or disagree with the following statement? Playing PE games teaches us about life. Use specific reasons and examples to support your answer. 2. Imagine that you have received some land to use as you wish. How would you use this land? Use specific details to explain your answer. What is Alcohol? Ethanol- the type of alcohol in alcoholic beverages Can be man made or naturally A depressant Slows down body central nervous system Can be lethal How Alcohol Works Once an alcoholic beverage is swallowed, the process of absorption begins How Alcohol Works Alcohol requires no digestion and passes readily through the walls of the small and large intestine How Alcohol Works 1/5 of alcohol consumed is absorbed in the stomach The major site of absorption is the small intestines Alcohol Equivalencies Alcohol Equivalencies •Wine •Beer •1 Glass •1 Can / Bottle •4 oz. •12 oz. •Distilled Spirits •1 Shot Glass •1.25-1.50 oz. •12% •4% •40% Alcohol by Alcohol by Alcohol by Volume Volume Volume •.48 oz •.48 oz •.50 oz Proof Proof refers to the percentage of pure alcohol in a beverage. For example, a 80-proof bottle of vodka is 40 percent alcohol. Factors that Influence Alcohol Absorption The greater the concentration, higher the proof, the greater the absorption rate. OR Factors that Influence Alcohol Absorption The more the alcohol consumed at one time, the longer the absorption period will be. Factors that Influence Alcohol Absorption Rapid consumption will result in an elevated Blood Alcohol Concentration Factors that Influence Alcohol Absorption The presence of food in the stomach delays the absorption of alcohol Factors that Influence Alcohol Absorption Heavier people have more body fluids in which alcohol is diluted Factors that Influence Alcohol Absorption Alcohol effects each individual differently Blood Alcohol Concentration •The amount of alcohol in the blood at any given time. Drinks Body Weight in Pounds 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 1 .04 .03 .03 .02 .02 .02 .02 .02 2 .08 .06. .05 .05 .04 .04 .03 .03 3 .11 .09 .08 .07 .06 .06 .05 .05 4 .15 .12 .11 .09 .08 .08 .07 .06 5 .19 .16 .13 .12 .11 .09 .09 .08 6 .23 .19 .16 .14 .13 .11 .10 .09 •In Virginia, anything over .08 is considered drunk. Tolerance More and more alcohol is required to produce an effect. Functions of Alcohol There are 4 functions that alcohol serves in our society 1-Social Mixer Alcohol is seen as the “Social Mixer” 2-Ritualistic Cultural ceremonies Religious ceremonies Marriage ceremonies Death 3-Dietary Essential part of one’s dietary intake; A complement to certain foods (i.e. wine) Ingredient in special food dishes (i.e. beer) 4-Mood Modification Used to satisfy personal needs; Reduce stress Feel high Feel confident Feel Popularity