* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heredity
Survey
Document related concepts
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
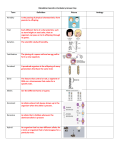
Cells and Heredity Study Guide for Life Science Chapter 3 – Sections 1 & 2 Quiz Section One Heredity – the passing of traits from parents to offspring Trait – each different form of a characteristic Genetics – the scientific study of heredity Self-pollination – pollen from a flower lands on the pistil (female sex cell) of the same flower Cross-pollinated – when two plants are crossed Purebred Organism – when the offspring of many generations have the same trait as the parent – example: TT, tt Gregor Mendel - performed two experiments on the garden pea plant “Father of Genetics” Mendel’s First Experiment – crossed a purebred tall plant with a purebred short plant first generation was all tall Mendel’s Second Experiment –allowed the first generation tall plants to self pollinate – second generation produced 3 tall plants and 1 short plant Gene – the factors that control a trait Alleles – the different forms of a gene Dominant allele – a trait that will appear in the offspring if one of the parents contributes it represented by a capital letter Recessive allele – a trait that must be contributed by both parents in order to appear in the offspring – an organism can carry the recessive trait and not show it is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present represented with a lowercase letter Hybrid Organism – has two different alleles for a trait – example: T Section Two Probability – the mathematical chance that an event will occur written as a fraction or a percent Punnett Square – a chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross can be used to determine the probability of a particular outcome Phenotype – an organism’s physical appearance or visible traits ex.: brown eyes or blue eyes Genotype – the genetic makeup or allele combination example: BB, Bb, bb Homozygous – an organism that has two identical alleles for a trait example: TT or tt Heterozygous – an organism that has two different alleles for a trait example: Tt There will be Punnett Square problems (word problems) on the quiz. Use the examples on the review worksheet for practice. Quizlet review for this quiz is available at: http://quizlet.com/67858324/mrs-weber-cms-7-cells-heredity-flash-cards/ or search "Mrs. Weber CMS 7 Cells & Heredity” The link is also on the science 7 page on my webpage.