* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HEART FAILURE
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
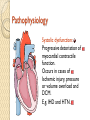
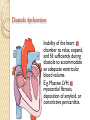
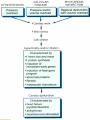
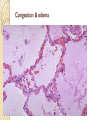
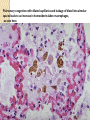
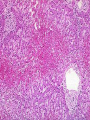
HEART FAILURE غفران أجياد ثامر فرح عماد HEART FAILURE A state that develops when the heart fails to maintain an adequate cardiac output to meet the demands of the body characterized by: 1. Diminished cardiac output (forward failure) 2. Damming back of blood in the venous system (backward failure) or Both . TYPES OF HEART FAILURE *Left sided ,right sided & biventricular heart failure *Acute &chronic heart failure *Compensated & decompensated heart failure * Forward & backward heart failure * Systolic & diastolic dysfunction Pathophysioylogy of H.F Before reaching H.F we have many mechanisms that is compensatory mechanisms : Adaptive mechanisms by which the CVS maintains arterial pressure & perfusion of vital organs : The Frank-Starling mechanism : >preload of .1 dilation helps to sustain cardiac performance by enhancing contractility. Myocardial structural change : Augmented .2 muscle mass (hypertrophy) with or without cardiac chamber dilatation. Activation of neurohumoral system : .3 Release of norepinephrine – >heart rate— augments myocardial contractility. Activation of renin – angiotensin – aldosterone system. Release of atrial natriuretic peptide. Pathophysiology Failure of adaptive mechanisms Heart failure Pathophysiology Systolic dysfunction: Progressive detoriation of myocardial contractile function. Occurs in cases of Ischemic injury, pressure or volume overload and DCM. E.g. IHD and HTN. Diastolic dysfunction: Inability of the heart chamber to relax, expand, and fill sufficiently during diastole to accommodate an adequate ventricular blood volume. E.g. Massive LVH, myocardial fibrosis, deposition of amyloid, or constrictive pericarditis. Pathophysiology The onset of HF is preceded by Cardiac hypertrophy : compensatory response of the myocardium to > mechanical work. The stimuli > the rate of protein synthesis, the amount of protein in each cell, size of myocytes, numbers of sacromeres & mitochondria : the mass & size of heart. Also accompanied by selective up regulation of several immediate early response gene & embryonic forms of contractile & other proteins. Schematic representation of the sequence of events in cardiac hypertrophy and its progression to heart failure, emphasizing cellular and extracellular changes LEFT SIDED HEART FAILURE Progressive damming of the blood within the pulmonary circulation and the consequence of diminished peripheral BP and flow. CAUSES : * IHD * SYSTEMIC HTN * MI * VALVULAR DISEASE * Non_ischemic myocardial disease MORPHOLOGY OF LEFT SIDED HEART FAILURE HEART: LEFT VENTRICLE is usually hypertrophied and often dilated Secondary enlargement of the left atrium LUNG: Pressure in the pulmonary veins are transmitted retrograde to the capillaries and arteries Pulmonary congestion & edema Heavy wet lung Kidney: Decrease cardiac output Reduction in renal perfusion Activation of renal – angiotensin –aldosterone System Retention of salt & water with consequent expansion of the interstitial fluid and blood volumes Pulmonary edema in lungs Brain: Hypoxic encephalopathy Congestion & edema Pulmonary congestion with dilated capillaries and leakage of blood into alveolar spaces leads to an increase in hemosiderin-laden macrophages, as seen here. RIGHT SIDED HEART FAILURE * Usually as a consequence of right sided heart failure * Cor pulmonale :chronic severe pulmonary hypertension due to increased resistance within the pulmonary circulation. * Other causes : multiple pulmonary emboli & valvular disease MORPHOLOGY OF RIGHT SIDED HERTE FAILURE HEART: Hypertrophy and dilation are generally confined to right ventricle and atrium. LIVER AND PORTAL SYSTEM: * Passive congestive hepatomegaly(nutmeg liver) * Centrilobular necrosis along with the sinusoidal congestion * Congestive splenomegaly * Ascites Here is an example of a "nutmeg" liver seen with chronic passive congestion of the liver. Note the dark red congested regions that represent accumulation of RBC's in centrilobular regions. the natural nutmeg is at right.