* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
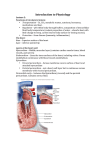
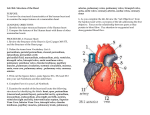
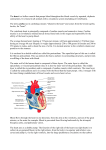
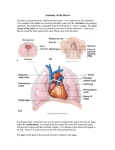
Introduction The blood must stay in motion to maintain homeostasis. The heart keeps blood moving. The volume of blood pumped by the heart can vary widely, between 5 and 30 liters per minute. An Overview of the Cardiovascular System The heart is a small organ; your heart is roughly the size of your clenched fist. Two closed circuits: Pulmonary circuit carries carbon dioxide—rich blood from the heart to the lungs and back Systemic circuit transports oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body and back The heart has four muscular chambers: Right and left atria collect blood returning to heart Right and left ventricles discharge blood into vessels to leave the heart The Pericardium The pericardium is the serous membrane lining the pericardial cavity, which surrounds the heart Visceral pericardium (epicardium) covers the heart’s outer surface Parietal pericardium lines the inner surface of the pericardial sac Structure of the Heart Wall Three distinct layers: Epicardium — covers the outside of the heart Myocardium — cardiac muscle Endocardium — lines the inside of the heart Orientation and Superficial Anatomy of the Heart The heart lies slightly to the left of the midline. The heart sits at an oblique angle to the longitudinal axis of the body. The heart is rotated slightly toward the left. The heart has external sulci that mark internal boundaries. Internal Anatomy and Organization of the Heart Pulmonary circuit Right atrium Tricuspid valve Right ventricle Pulmonary valve Pulmonary trunk Systemic circuit Left atrium Mitral valve Left ventricle Aortic valve Aorta Clinical Note Internal Anatomy and Organization of the Heart The Cardiac Cycle All of the electrical and mechanical events that take place during one heart beat are referred to as one cardiac cycle. Systole — contraction Diastole — relaxation The Electrocardiogram (ECG) The ECG is a recording of the electrical events in the heart. P wave — atrial depolarization QRS complex — ventricular depolarization T wave — ventricular repolarization