* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mag Fields Pres New
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
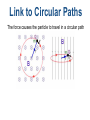
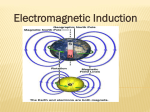
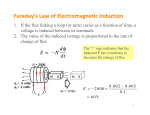
Bill and Bev Force on a Moving Charge The force on a charge q, is F = Bqv where v is the velocity B q F v Link to Circular Paths The force causes the particle to travel in a circular path Link to Circular Paths F = Bqv F= 2 mv r Bqv = 2 mv r r = mv Bq The radius of curvature depends on the strength of the field, the mass of the particle, the charge of the particle and the velocity. Mass Spectrometer Link to Circular Paths T = 2pir v r = mv Bq T = 2 pi m BQ Questions -31 A particle of mass 9.1 x 10 kg and with a charge of 1.6 x 10-19 C, is moving at 4.5 x 106 ms-1. It enters a uniform magnetic field of flux density 0.15 mT at 90 degrees. What is the radius of its circular path. Magnetic Flux The magnetic flux density (B) x the area swept out (A) = magnetic flux (theta) Units Webber Electromagnetic Induction A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force Therefore moving a conductor in a (to make it move). field will cause a current to flow. This is electromagnetic induction. Or a varying magnetic field over a conductor will also cause a current. Electromagnetic Induction Flux cutting. The conductor has to cut field lines for an emf to be induced. Magnetic Flux Linkage Through a coil of N turns n theta = n BA when the magnetic field is along the normal (perpendicular) of the coil face the N theapta = NBA - When the coil is turned 180 then N theta = -NBA - When the magnetic field is parallel to the coil flux linkage = 0 - Faraday's Law The induced emf in a conductor is equal to the rate of change of flux linkage through the circuit. 1. Write this out as an equation. 2. Derive the equation from V= W/Q