* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 17: Magnetic induction: Faraday`s law
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
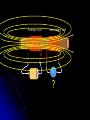
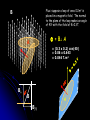
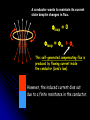
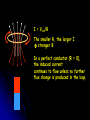
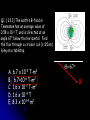
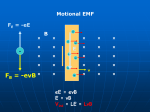
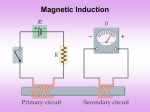
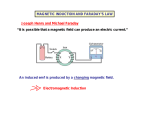
Phy2005 Applied Physics II Spring 2016 Announcements: Syllabus error: read rest of Ch. 22 (DC motors, etc.) Science news page “The flight of the sea snail” NYT link to article Last Time Michael Faraday invented DC motor DC motor activity Last time cont’d Solenoid: how to make a nearly constant magnetic field B For infinitely long solenoid with tight coils, inside B = monI (const.!) n: number of turns/m Note: for such a solenoid B=0 outside Today: magnetic induction INDUCTION Michael Faraday (1791 – 1867) …it appeared very extraordinary, that as every electric current was accompanied by a corresponding intensity of magnetic action at right angles to the current, good conductors of electricity, when placed within the sphere of this action, should not have any current induced through them, or some sensible effect produced equivalent in force to such a current.” Primary Coil Secondary coil G ? Summary of Experimental Findings EMF (voltage) is induced in the secondary coil Only when the magnetic field through it changes. EMF induced is bigger if the area of coil is bigger. EMF is induced always in the opposite direction of change in magnetic field. Vind = - A (dB/dt) rate of ch of B with time = - d/dt (rate of ch of with time) = B A: magnetic flux (A is cross-sectional area to field) Flux: suppose a loop of area 0.2m2 is placed in a magnetic field. The normal to the plane of the loop makes an angle of 40o with the field of B=0.3T. B = B┴ A A = (0.3 x 0.2) cos(40) = 0.06 x 0.643 = 0.046 T.m2 B┴ B A B// 1 loop + + + + - Vind = - d/dt Vtot = -3 d/dt Net number of loops Example 23.2 150 turn loop with a 0.75 cm2 cross-section Magnetic field: 0 T 0.25 T in 3.6 s 5 Ohm What is the induced current in the coil? Persistence: The action or fact of persisting in a particular state, opinion, purpose, or course of action, esp. despite opposition, setback, or failure; the quality or virtue of being persistent. Issac Newton: INERTIA Newton’s First Law An object will remain its state (at rest or in motion) provided that no external net force acts on the subject. A conductor wants to maintain its current state despite changes in flux. loop = 0 loop = m + s This self-generated compensating flux is produced by flowing current inside the conductor (Lenz’s law). However, the induced current dies out due to a finite resistance in the conductor. I = Vind/R The smaller R, the larger I stronger B In a perfect conductor (R = 0), the induced current continues to flow unless no further flux change is produced in the loop. AC Generator http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/motorac.html#c2 ACADEMIC HONESTY Each student is expected to hold himself/herself to a high standard of academic honesty. Under the UF academic honesty policy. Violations of this policy will be dealt with severely. There will be no warnings or exceptions. Q1. ( 23.3) The earth’s B-field in Tennessee has an average value of 0.58 x 10-4 T, and is directed at an angle 67o below the horizontal. Find the flux through a circular coil (r=20cm) lying on a tabletop. A. 6.7 x 10-2 T-m2 B. 6.7×10-6 T-m2 C. 1.6 x 10-2 T-m2 D. 1.6 x 10-4 T E. 8.3 x 10-14 m2 Q=67o B