* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
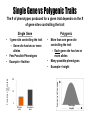
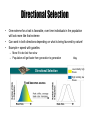
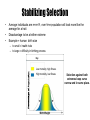
Biology Evolution II Notes Evolution and Populations Darwin’s Ideas Revisited • Developed his theory of natural selection which explains how species evolve • Published theory in 1859 • Gregor Mendel’s findings were published in 1860 and the significance of Mendel’s work was not realized until after 1900 • Without knowledge of genetics Darwin was unable to explain two factors that were key to understanding evolution – What is the source of variation? – How are inheritable traits passed on from one generation to the next? • Scientists were able to combine Darwin’s theory with basic principles of genetics in 1910. Gene Pools • Gene Pool = combined genetic information of all members of a population – Typically contains two or more alleles for a trait • Relative Frequency = how often an allele occurs within the gene pool compare to other alleles – Usually expressed as a decimal or a percentage % – All alleles for a trait must add up to 1 or 100% Practice Problem: In a population of people there are a total of 35 blue alleles, 40 brown alleles, and 25 green alleles. What is the relative frequency of each allele within the gene pool? Lethal Recessive Alleles in Gene Pools • How are lethal recessive alleles maintained within a gene pool? Sources of Genetic Variation Mutations • • Gene Shuffling Change made in DNA Sequence • – Change does not always affect organisms phenotype • Changes that do affect an organisms phenotype may also affect an organisms fitness – Can make an organism more or less likely to survive and reproduce successfully – Give examples of mutations affecting an organisms phenotype that would make them more and less successful! Most inheritable differences are due to gene shuffling Chromosomes assort randomly during meiosis resulting in new combinations of genes – Sexual Production therefore can produce many genetic differences between you, your parents, and your siblings Is Genetic Variation In a Species Good or Bad? • Good! Why? • When natural disasters or changes in the environment occur, it is more likely for some members of the species to survive because they may have a variation that allows them to survive the change (adaptation). Single Gene vs Polygenic Traits The # of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends on the # of gene sites controlling the trait Single Gene Frequency of Phenotype (%) • • 1 gene site controlling the trait – Gene site has two or more alleles Few Possible Phenotypes Example = Hairline • • • More than one gene site controlling the trait – Each gene site has two or more alleles Many possible phenotypes Example = height 100 50 0 Widow’s peak No widow’s peak Frequency of Phenotype • Polygenic Phenotype (height) Natural Selection On Single-Gene Traits • • • Leads to changes in allele frequencies and thus evolution (changing) of the species Less complex than polygenic traits Give Example! Natural Selection On Polygenic Traits •Wide range of phenotypes for a trait •Natural selection can act in 3 ways •Directional Selection •Stabilizing Selection •Disruptive Selection Directional Selection • • • One extreme for a trait is favorable, over time individuals in the population will look more like that extreme Can work in both directions depending on what is being favored by nature! Example = speed with gazelles – More fit to be fast than slow – Population will get faster from generation to generation Directional Selection Food becomes scarce. Key Low mortality, high fitness High mortality, low fitness Stabilizing Selection • • • Average individuals are more fit, over time population will look more like the Stabilizing Selection average for a trait Disadvantage to be at either extreme Example = human birth size – to small = health risks – to large = difficulty in birthing process Key Low mortality, high fitness High mortality, low fitness Birth Weight Selection against both extremes keep curve narrow and in same place. Disruptive Selection Disruptive Selection Largest and smallest seeds become more common. Key Low mortality, high fitness High mortality, low fitness Population splits into two subgroups specializing in different seeds. Beak Size Number of Birds in Population • Either is extreme is more favorable than being average, over time population will look like both extremes with less individuals exhibiting the average trait Individuals being average for a particular trait are at a disadvantage Number of Birds in Population • Beak Size Genetic Drift • Random change due to chance (not natural selection) – Most likely to occur in a small populations Founder Effect- small group separate from main group -gene frequencies differ from main group Bottleneck Effect- large number of indivuals die off. -gene frequencies by chance (not selection) are different from original group