* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Genetics PPT
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
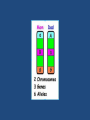
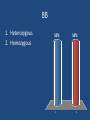
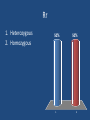
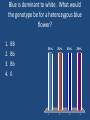
INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS TRAITS • Traits are the different forms of a characteristic that you may exhibit • Ex: Blue or Brown Eyes • Traits are inherited from our parents – mother and father • Therefore, when we talk about genetics, we are talking about sexual reproduction Chromosomes • Every cell in a human body has 23 pairs of chromosomes – half from our mother, half from our father • Genes are found on chromosomes • We have about 20,000-25,000 genes • Each gene holds a code that tells our body to make a certain protein • The protein that is made determines a Specific trait. Ex: Blue eye pigment or Brown eye pigment • Alleles • The different forms of a gene that can exist • Ex: Curly hair gene or straight hair gene • Dominant – ‘Strongest Allele’ – If it is present, you will have that trait. We use upper case letters for dominant alleles • Recessive – ‘Weakest Allele’ – This won’t show up unless there are two of them. We use lower case letters for recessive alleles Human cells contain ____ chromosomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 23 46 12 2 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 DNA contains a code that tells your body to make _____________ 1. fat 2. carbohydrate 3. protein 33% 1 33% 2 33% 3 ______________ traits won’t show up unless you have two copies of the gene. 25% 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% 25% 25% Recessive Dominant Generic Terrific 1 2 3 4 Genotype • The actual alleles you have for a trait • Ex: For eye color, you inherit B from dad and b from Mom • Your genotype is Bb • If there is a dominant allele, the genotype is written with the upper case first. (Never write bB) • Always use the same letter for both alleles • Your genotype is the genes you have Genotype (cont’d) • If you have two copies of the same allele for a trait (BB or bb), then you are HOMOZYGOUS for that trait. • If you have two different alleles for a trait (Bb), then you are HETEROZYGOUS for that trait Phenotype •How the genes actually show up, or how they are expressed •So, if your genotype is Bb, • Where B is brown • And b is blue •The phenotype would be Brown eyes •Phenotype is the physical appearance BB 1. Heterozygous 2. Homozygous 50% 1 50% 2 Rr 1. Heterozygous 2. Homozygous 50% 1 50% 2 You inherit the gene for freckles (F) from your mother, and the gene for no freckles (f) from your father. What is your genotype? 1. 2. 3. 4. Freckles No freckles Ff FF 25% 1 25% 2 25% 3 25% 4 You inherit the gene for freckles (F) from your mother, and the gene for no freckles (f) from your father. What is your phenotype? 25% 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% 25% 2 3 25% Freckles No freckles Ff FF 1 4 Blue is dominant to white. What would the genotype be for a white flower? 25% 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% 25% 25% BB Bb bb 0 1 2 3 4 Blue is dominant to white. What would the genotype be for a heterozygous blue flower? 1. 2. 3. 4. BB Bb Bb 0 25% 1 25% 2 25% 3 25% 4 Karyotype – Normal/Male A picture of the chromosomes found in an individual. Used to determine abnormalities. Karyotype – Abnormal/Female There are three copies of chromosome 21 – there should only be two copies. This is a karyotpe of a female with Down’s Syndrome.