* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TODAY*s OBJECTIVES:
Survey
Document related concepts
Joseph's Granaries wikipedia , lookup
Memphis, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Art of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Women in ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
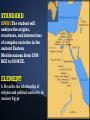
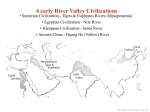
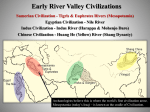
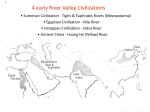
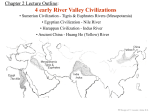
STANDARD SSWH1 The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BCE to 500 BCE. ELEMENT b. Describe the relationship of religion and political authority in Ancient Egypt. PP Design of T. Loessin; Akins H.S. GEOGRAPHY • • • • • • Settlements along Nile surrounded by deserts Protection and isolation Narrow strip of fertile land Yearly flooding, but predictable Intricate network of irrigation ditches Worshiped as a god – giver of life and benevolent Upper and Lower Egypt • • • • • • Lower Egypt = Delta Where most of Egypt’s history focused Upper Egypt developed later upstream Nile provided reliable transportation to go north, drift with the current toward the sea to go south, sail catching the Mediterranean breeze PP Design of T. Loessin; Akins H.S. EARLY DYNASTIC PERIOD 2920-2575 BCE • Unification of Upper and Lower Egypt by Menes in 3,100 B.C.E. • Foundation of the capital Memphis. • Early Step Pyramid is built at Saqqara. • Unlike Sumeria, no independent city-states in Egypt • Creates first Egyptian dynasty Step pyramid at Saqqara Pharaoh [royal house] the ruler of Egypt • were considered gods; served both political and religious roles • Ruled under a Theocracy • Pharaoh’s thought to rule after death • All possessed the eternal spirit of ka • As Gods = full responsibility for Egypt’s well-being. PP Design of T. Loessin; Akins H.S. The pharaoh Akenaton and his wife-sister Nefertiti worshiping the sun god, Ra. OLD KINGDOM 2660-2180 BCE • pyramids = tombs, place of rule • The Great Pyramids built at Giza. • Created a bureaucracy: an administrative organization with officials and regular procedures • Bureaucracies helped Pharaohs. • Vizier- most important official and reported directly to the Pharaoh. PP Design of T. Loessin; Akins H.S. The Great Pyramids at Giza. MIDDLE KINGDOM 2180-1550 BCE Central power collapses Lower Egypt: Invaded by Hyksos Asiatic people who used • horse drawn chariots • bronze tools and weapons • Upper Egypt • dominated by kings in Thebes. • • • • NEW KINGDOM 1550-1070 BCE • Theban King Ahmose = expelled the Hyksos and reunites Egypt. • Memphis now main residential city. • Ramses II (1290- 1224 BC) divides power in Middle East with the Hittites • Qantir capital of Egypt. • Tutankhamen restored the old gods when Ramses died. • Invasions of mysterious sea peoples wreck havoc throughout Mediterranean region. PP Design of T. Loessin; Akins H.S. RELIGION • Polytheistic: Over 2,000 gods • Ra, the sun god; Horus, sky god; Anubis, god of embalming; Isis, mother goddess “giver of life” associated with Nile • Belief in an afterlife. Pharaoh's often buried with servants, food, and items they would need to rule. • The dead were judged by Osiris, god of the dead. • Mummification rituals for Pharaohs and extremely wealthy PP Design of T. Loessin; Akins H.S. Above: The pantheon of Egyptian gods* Social Structure Socially Mobile classes • • • • • • Women treated respectfully. Retained property and inheritance rights when married. In charge of household and education of their children. Some operated businesses. Upper class women could become priestesses 4 queens became Pharaohs. • Men and women wore makeup Bulk of population = • Kohl- dark lined eyes in artwork peasants who farmed the • Both genders wore lipstick land. PP Design of T. Loessin; Akins H.S. Merchants traded up and down the Nile as well as w/other countries. Egyptian Writing • Pictographs developed into hieroglyphics (priest carvings/sacred writings” • Written on Papyrus, unfurled reed from the Nile, dried into strips • The Rosetta Stone was discovered in 1799 A.D. and was instrumental in deciphering hieroglyphics • Hieratic script was a simpler version of hieroglyphics and used for business and daily life. PP Design of T. Loessin; Akins H.S. SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY • Geometry • Base 10 numeric system (decimal) • engineers and architects, first to use stone columns • Calendar • Amazing advancements in medicine: • Mummification • splints, bandages, • compresses for fractures, wounds, and disease. PP Design of T. Loessin; Akins H.S. STANDARD SSWH1 The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BCE to 500 BCE. ELEMENT b. Describe the relationship of religion and political authority in Ancient Egypt. List five points that will help you explain this standard/element: • • • • •