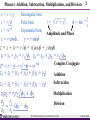* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt - Weber State University
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Music technology wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Plug-in electric vehicles in Germany wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
History of the electric vehicle wikipedia , lookup
Electric vehicle wikipedia , lookup
Transmission tower wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
0
EE 1270: Introduction to Electric Circuits
Lecture 18:
Phasors
Chapter 9: Sinusoidal SteadyState Analysis
Section 9.3, 9.4
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
Suketu Naik
Representation of Complex Numbers
1
Rectangular Form (real and imaginary)
a jb; j 1
Imaginary
Polar Form (magnitude and phase)
c
Real
Exponential Form
ce
j
c cos j sin
c a b
a c cos ; b c sin
1 b
tan
a
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
2
2
Suketu Naik
2
Phasors
v Vm cost Re{Vm e
j (t )
j
jt
} Re{Vm e e }
V Vm e j Vm
Phasor Transform or
Phasor Representation
1) A phasor is a complex number that represents the
amplitude and phase of a sinusoid
2) Phasors provide a simple means of analyzing linear
circuits excited by sinusoidal sources
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
Suketu Naik
Phasors: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division
3
Amplitude and Phase
Complex Conjugate
Addition
Subtraction
Multiplication
Division
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
Suketu Naik
Phasors
4
v Re{Vm e j e jt }
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
Suketu Naik
Example 9.5: Hard Way
5
Problem
Solution
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
Suketu Naik
Example 9.5: Easy Way
6
Problem
Solution
Use Phasors
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
Suketu Naik
AP 9.1, AP 9.2
7
1090
V
518
(e)(5545)(0.1 45)mA
(d )
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
Suketu Naik
Phasor Notation for Resistor
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
8
Suketu Naik
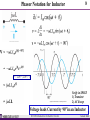
Phasor Notation for Inductor
9
Verify in SPICE
1) Transient
2) AC Sweep
Voltage leads Current by 90° in an Inductor
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
Suketu Naik
Phasor Notation for Capacitor
10
i CVm sin( t V )
I CVm e j (V 90)
CVm e jV e j 90
jCVm e jV
jCV
Verify in SPICE
1) Transient
2) AC Sweep
Current leads Voltage by 90° in a Capacitor
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
Suketu Naik
Impedance and Reactance
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
11
Suketu Naik
AP 9.3, AP 9.4
EE 1270 Introduction to Electric Circuits
12
Suketu Naik