* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PACK 3 - Speyside High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
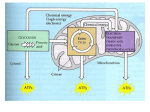
Page 1 PACK 3 CELL BIOCHEMISTRY PART 1 OBJECTIVES At the end of this unit you should be able to: 1. Describe the outline chemical structure of carbohydrates and lipids. 2. Describe the role of carbohydrates in energy production and energy reserves and outline the respiratory process. 3. Explain muscle fatigue in terms of lactic acid build up and reduction of ATP. 4. List at least 5 cell processes requiring energy. 5. Describe the functions of lipids as hormone components, protective devices and reserve energy supply. PRACTICAL WORK 1. Compulsory Practical Identification of various carbohydrates. 2. Determination of energy content of various foods. Page 2 PACK 3 CELL BIOCHEMISTRY (1) The cell can be thought of as a small chemical plant, manufacturing an enormous range of end products. The process of synthesising these end products must be carefully controlled so that energy and raw materials are not wasted. The main products fall into three biochemical groups, the Carbohydrates, the Lipids and Proteins. Read your text book pages 36-41 and make up your own notes. ACTIVITY SAQ 1 1. Name the three groups of carbohydrates. 2. Name the three chemical elements which are combined to form carbohydrates. 3. Name two monosaccharides. 4. Which chemical reaction is used to split a disaccharide into two monosaccharides? 5. Name two disaccharides. Page 3 6. Why are polysaccharides insoluble in water? 7. Glycogen is one of the major storage materials of the human body. name two of the major storage areas in the human body for this material. 8. Why is Glycogen a good storage material. 9. What is the function in the body of all carbohydrates? METABOLISM AND RESPIRATION The sum total of All chemical reactions going on inside cells is called Metabolism. Some of the chemical reactions are Catabolic and involve the breakdown of large molecules into smaller, simpler ones -e.g. digestion; respiration. Many of these reactions are Exergonic - in other words they liberate energy. Some chemical reactions are Anabolic and involve the building of complex molecular structures from simpler ones - eg Protein synthesis; amino acid synthesis. These reactions are Endergonic - they need energy. Living things have the ability to link these energy consuming and energy producing reactions together using an energy “currency” molecule called ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE (ATP) This can be thought of as energy money - if a cell needs to carry out work it must “spend” some of its energy currency. If a cell is bankrupt it dies - it has no energy currency to spend. The energy demand by living cells is small but continuous. In addition the release of energy must be controlled and orderly. Page 4 Read your text book pages 29-34 and make up your own notes. ACTIVITY SAQ 2 1. What is meant by phosphorylation? 2. The bond holding the last inorganic phosphate on to Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) is said to be a high energy bond. What do you think this term means? 3. Which process is involved in the controlled release of energy from Glucose? 4. What name is given to the initial process of glucose breakdown and where in the cell are the chemical steps undertaken? 5. What is the end product of this first stage of respiration? 6. This first stage of respiration is ANAEROBIC. What does this term mean? 7. What is the net gain in ATP molecules of this stage? Page 5 8. If human muscle cells work extremely hard, the supply of oxygen to the cells is sometimes inadequate. Into which material is the Pyruvic Acid converted? 9. After a race, the breathing rate never returns to the resting rate at once. Lactic Acid is removed from the muscles and transported to the Liver. Extra oxygen taken in after the period of exercise is used to metabolise this Lactic Acid. What name is given to this quantity of oxygen? 10. If sufficient oxygen is present the Pyruvic Acid from Gycolysis is fed into which cycle? 11. In which cell organelle do the next series of reactions take place? 12. What name is given to the jelly like interior of this cell organelle? 13. What name is given is given to the folds of internal membranes in these organelles and why are they so important? 14. Pyruvic Acid is first converted to Acetyl CoEnzyme A. This involves the loss of carbon and of hydrogen. Name the carrier which “mops” up the hydrogen. Page 6 15. Which biological catalysts are involved in the removal of hydrogen and carbon from the compounds of the KREBS’ CYCLE? 16. Name the stalked enzyme packets located on the mitochondrial cristae to which the hydrogen is transferred. 17. What is oxidative phosphorylation? 18. How many molecules of ATP can be produced from one turn of the Krebs’ Cycle? 19. How many molecules of ATP can be released from the complete oxidation of one glucose molecule? 20. What is the final hydrogen acceptor and which metabolic compound is formed? 21. By which process may this compound leave the cell? 22. Which enzyme is involved in “sticking” oxygen to hydrogen to form water? 23. Certain poisons work by blocking the action of this enzyme. Explain briefly why these poisons will kill you. Page 7 ACTIVITY Try to answer the questions on page 34-35 of your ACTIVITY Try the following multiple choice questions. text. SAQ 3 1. Which statement about Adenosine Triphosphate is Not true: a) b) c) d) It is formed only under anaerobic conditions. It is used as the energy currency of the cell. The formation of ATP is an endergonic reaction. Some ATP is used in the synthesis of storage materials. 2. Oxidation and reduction: a) b) c) d) Involve the gain and loss of proteins. Are defined as the gain of electrons. Always occur together. Take place under anaerobic conditions. 3. Glycolysis: a) b) c) d) Involves no ATP production. Takes place in the mitochondria. Is the same thing as fermentation. Only takes place in muscle cells. 4. Fatty Acids from lipid breakdown can be fed into the Krebs’ Cycle as: a) b) c) d) Pyruvic Acid. Citrus Acid. Acetyl CoEnzyme A. Glucose. Page 8 Read your text book pages 39-40 and make up your own notes. ACTIVITY SAQ 4 1. Name the four groups of lipids. 2. What characteristic do all lipids have in common? 3. What is a triglyceride? 4. What is a phospholipid? 5. In the diagram below, name the parts labelled A and B. Page 9 6. What is a Phospholipid and why are they so important in the structure of cell membranes? 7. What is a steroid? 8. Name two uses of steroids in the human body. 9. What is the main use of fat in the human body? 10. List 6 other uses of lipids in the body. 11. Intensive training reduces the body fat considerably. Very often women athletes stop menstruating. Can you explain why? Page 10 ANSWERS TO SAQs PACK 3 CELL BIOCHEMISTRY (1) SAQ 2 1. Phosphorylation is the addition of inorganic phosphorus to ADP to produce ATP. 2. When the bond is broken energy is released. 3. Respiration (aerobic) 4. Glycolysis. The enzymes are located in the cell cyctoplasm. 5. Pyruvic Acid. 6. Proceeds without the use of oxygen. 7. Gain of 2ATP for every glucose molecule used. 8. Lactic Acid. 9. Repaying the Oxygen Debt. 10. Krebs’ Cycle (or Citric Acid cycle or Tricarboxylic Acid cycle) 11. Mitochondrion. 12. Matrix. 13. Cristae - provide a large surface area for the attachment of Cytochrome enzymes. 14. NAD - Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. 15. Enzymes - dehydrogenases and decarboxylases. 16. Cyctochrome enzymes. 17. Transfer of Hydrogen along the cytochrome chain releasing energy trapped which is then trapped in the structured of ATP. Page 11 18. ATP for each Pyruvic Acid molecule. 19. ATP from Gylcolysis + 36 from Krebs’ Cycle = 38 ATP from each Glucose. molecule. 20. 21. Oxygen is the final Hydrogen acceptor and the product is water. Osmosis 22. Cytochrome oxidase. 23. If Cytochrome oxidase is blocked then the Cytochrome chain becomes blocked with hydrogen. The Hydrogen acceptor NAD in turn cannot offload its hydrogen and so hydrogen cannot be unloaded from the Krebs’ Cycle reactions. The Cycle halts - no energy produced. SAQ 4 1. Fats, Oils, Steriods and Phospholipids. 2. Insoluble in water. 3. Molecule of glycerol attached to three molecules of fatty acids. 4. A triglyceride with one fatty acid replaced by a phosphate group. 5. A is Glycerol. B is a Fatty Acid. 6. Phospholipids are both hydrophobic and hydrophilic and so can form a waterproof barrier between the “wet” inside of a cell and the “wet” outside. 7. Steriods are a group of lipids consisting of three 6-Carbon rings joined to one 5-Carbon ring. 8. Sex hormones and bile. 9. Energy reserve. 10. Thermal insulation; nerve insulation; padding and protection; Vitamin absorption and transport; sex hormones; cell membrane component. Page 12 11. Lack of cholesterol to manufacture the sex hormones oestrogen and progesterone. SAQ 1 1. Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and Polysaccharides. 2. Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen. 3. Glucose, Fructose and Ribulose. Page 13 Hydrolysis. 4. Sucrose, Lactose and Maltose. 5. Very large molecules and so insoluble. 6. Muscle and liver. 7. Glycogen is insoluble and has no osmotic effects in cells. 8. Energy production. Carbohydrates are the fuel used in Respiration. SAQ 3 1. 2. 3. 4. (a) (c) (c) (c) Page 14