* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
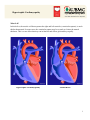
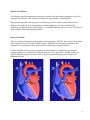
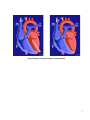
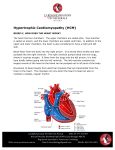
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy What Is It? In this defect, the muscle wall that separates the right and left ventricles (ventricular septum), is much thicker than normal. In some cases, the ventricular septum may be as much as 4 times the normal thickness. This is a rare defect that may run in families and affects girls and boys equally. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Normal Heart 1 What Are Its Effects? The enlarged ventricular septum may obstruct the outlets to the aorta and/or pulmonary artery (PA), causing a heart murmur. This is known as Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Many patients experience no symptoms except during periods of exertion, when chest pain and shortness of breath may occur. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may also cause fainting spells, arrhythmia (irregular heart beat), heart failure, or even death. Patients with severe cases are at risk of dying suddenly from abnormal heart rhythms. How Is It Treated? There are various treatments for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, or HOCM. These include medications such as beta blockers and calcium channel blockers, which slow the heart rate and minimize the symptoms. For most patients, these medications are sufficient for a normal lifestyle. For those patients with more serious symptoms or an intolerance for medication, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may be treated by slowing the heart rate with a pacemaker. Another option is the surgical reduction (septal myectomy) of the ventricular septum during open heart surgery (see illustrations below). 2 Surgical Repair of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy 3