* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download T/F 1. Pyruvate, the end product of glycolysis, is processed
Survey
Document related concepts
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
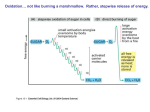
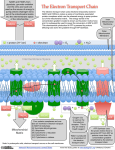
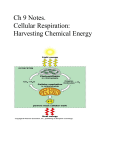
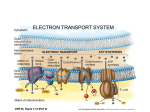
T/F 1. Pyruvate, the end product of glycolysis, is processed differently in the presence and absence of oxygen 2. In lactic acid fermentation pyruvate is reduced to pyruvic acid. 3. In ethanol fermentation, pyruvate is converted to acetaldehyde which is reduced to ethanol 4. During fermentation NAD+ is educed to NADH, allowing glycolysis to proceed 5. Glycolysis is an ancient biochemical pathway that was likely used in the common ancestor of all living organisms today. 6. How many molecules of CO2 are produced for each molecule of glucose that passes through glycolysis and the Krebs cycle? a. 2 b. 3 c. 6 d. 7 7. The electrons generated from the Krebs cycle are transferred to ____________ and then are shuttled to _______________. a. NAD+ / oxygen b. NAD+ / electron transport chain c. NADH / oxygen d. NADH / electron transport chain 8. The electron transport chain pumps protons a. out of the mitochondrial matrix. b. out of the intermembrane space and into the matrix. c. out of the mitochondrion and into the cytoplasm. d. out of the cytoplasm and into the mitochondrion. 9. All of the following statements about cytochromes of the electron transport chain are true except a. b. c. d. e. They are heme proteins They serve as electron carriers in oxidation-reduction reactions They all have the same energy when reduced When reduced, iron is in the +2 state When oxidized, iron is in the +3 state 10. The function of an electron in the electron transport chain is a. To transfer energy from complex II to complex I b. To pump hydrogen ions using complex II c. To use its free energy to pump protons against their concentration gradient d. To combine with phosphate when ATP is synthesized e. To react with ATP synthase 11. Which of the following statements about the electron transport chain is NOT correct a. b. c. d. e. It is located in the inner mitochondrion membrane Cytochrome c accepts electrons from complex II Cytochrome oxidase (complex IV) accepts electrons from Cytochrome c Complex I is called NADH dehydrogenase Coenzyme Q accepts electrons from complex I and complex II 12. What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain? a. Water b. Oxygen c. Carbon dioxide d. NAD+ e. FAD 13. Which membrane is the location of ATP synthase? a. The cell membrane b. The nuclear membrane c. The outer mitochondrial membrane d. The inner mitochondrial membrane e. The ribosomal membrane 14. How many carbon atoms are present in glucose and in pyruvate? 15. Why do plants typically store their excess energy as carbohydrates rather than fat? 16. How much energy would be generated in the cells of a person who consumed a diet of pyruvate instead of glucose? Calculate the energy generated on a per molecule basis.