* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 2201 Name: Limits to Cell Size
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
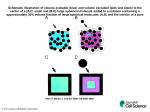
Biology 2201 Name:________________ Limits to Cell Size Introduction Why can’t cells continue to grow larger to become giant cells? Why are most cells, whether they’re from an elephant or an earthworm, about the same size? Why would cells continually grow and divide to become two smaller cells? Purpose To simulate the changing relationship of surface area to volume for a growing cell. Materials 3 spherical items Tape or string Calculator Procedure This activity is designed to give you a hands-on appreciation of the relationship between surface area and volume which is so critical to understanding the limits of cell growth. 3 cubic items Ruler Before you begin, you will need to find 3 spherical and 3 cubic objects in your house or around the school. It doesn’t matter if they are perfectly spherical or cubic; we will just assume they are in all calculations. These three spheres and cubes represent growing cells. Design a table and present the results of 1-8 in your table: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Find the circumference of the three spherical objects. Use a piece of string or tape to measure. Calculate the radius of each one using the formula C=2Br Find the surface area of each using the formula SA= 4Br2 Find the volume of each one using the formula V=4B3/3 Calculate the ratio of surface area to volume Ratio=SA/V Now find the surface area of the cubic objects SA=6(l x w) Find the volume of the cubic objects V= l x w x h Calculate the ratio of surface area to volume Ratio=SA/V ( Table values will vary according to objects chosen) Analysis 1. If the spherical objects represent growing animal cells, which cell has the greatest surface area? Greatest volume? (Answers will vary) 2. If the cubic blocks represents growing plant cells, which cell has the greatest surface area? Greatest volume?(Answers will vary) 3. Which spherical object has the greatest SA/V ratio? Which block? (Answers will vary, but the smallest should have the greatest) 4. What happens to the SA/V ratio as the cell grows (gets bigger)? (As the cell gets larger, the SA/V ratio decreases ) 5. How will growth in an animal cell affect cell processes? (Think: osmosis and diffusion) (If the cell is too big, the surface area will not be large enough to permit everything to diffuse through the increased volume of the cell) 6. Which size in both plant and animal cells is most efficient at permitting materials to enter and leave the cell? ( the smallest ) 7. Write a summary statement explaining how SA/V ratio limits growth of an individual cell. (Once the available SA cannot permit substances to diffuse throughout the entire volume of the cell, the cell will suffer, the cell must divide before this point is reached )