* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO 202 STUDENT LECTURE NOTES Lecture: Heart l Heart
Survey
Document related concepts
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
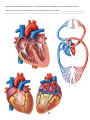
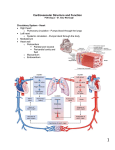
BIO 202 STUDENT LECTURE NOTES Lecture: Heart l Heart – located in the mediastinum What is the mediastinum? ___________________________________________________________________________ The heart sits mainly to the _____________ of midline and is rotated so its ___________ side is more anterior. What is anterior to? _________________________ posterior to? _______________________ Where is its superior border relative to the ribs? ______________________inferior border? _______________________ Size? ___________________ What is the apex? __________________________ the base? _______________________ Pericardium Describe this two layered sac __________________________________________________________________________ The parietal layer of the serous pericardium is located where? _______________________________________________ The visceral layer of the serous membrane is located where? ________________________________________________ So what is the pericardial cavity and what is normally found there? ___________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Name the three layers of the heart wall and what they are composed of: 1. ________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________________________________________________________________________ Cardiac muscle tissue – cardiac muscle cells / fibers shape of cells ________________ number of nuclei per cell ________________ striated? _______________________ voluntary? _______________________________ junctions between cells called _________________________ …..and what two types of special cell junctions are found here?___________________________________________________________________________________________ Cells are arranged in bundles that are ______________________________. What kind of motion does this produce when it contracts? _____________________________________________ Connective tissue wraps around and bundles cardiac muscle fibers like it did around skeletal muscle fibers. What is the CT sheath that surrounds the cardiac muscle fibers called? ________________________________ It contains collagen fibers, lots of capillaries,and nerves What is the fibrous skeleton? ________________________________________________________________________ What are some of its functions? ______________________________________________________________________ Know these structures and be able to label them on an image: - also know how blood flows through the heart and how the valves open and close as the heart contracts / relaxes left and right atria – atria are the _______________________chambers; between them is the ______________ septum left and right ventricles – ventricles are the ______________ chambers; between them is the _____________ septum auricles; pectinate muscles; trabeculae carneae; papillary muscles superior vena cava; inferior vena cava; four pulmonary veins; aorta; pulmonary trunk; left and right pulmonary arteries arteries contain blood moving _________ from the heart; veins contain blood moving _______________ the heart right atrioventricular valve = __________________ valve left atrioventricular valve = ______________ valve = _______________ valve chordae tendinae right semilunar valve = _____________________________ left semilunar valve = ______________________________ Differences in design of AV valves and SL valves? __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Pulmonary and Systemic blood circulation – know how blood flows through these circuits and through the heart - Why is the left ventricular heart wall thicker than the right ventricular heart wall? ______________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Coronary Circulation Know these and be able to identify on an image: Three grooves on the heart ___________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ · Coronary arteries – originate where? __________________________________________________________________ Left Coronary artery – two branches: 1. ______________________________ 2. ________________________________ Right coronary artery – two branches 1. ______________________________ 2. ________________________________ · Cardiac veins – drain into large, transverse posterior vein called the ___________________________ sinus which opens into the ____________ _____________ Three cardiac veins: 1. ________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. ________________________ Heart attack – often caused by what? __________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ Also define: thrombus ______________________________________________________________________________ ischemia _______________________________________________________________________________ infarct _________________________________________________________________________________