* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Experience 2 Follow-up 1. Answer the following
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
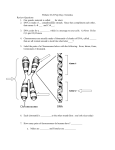
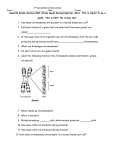
Biol&160 Experience 2 Follow-up Name: ________________________________________ 1. Answer the following questions about this normal eukaryotic cell in the process of dividing: What type of division is shown here? What phase of division is shown here? What is this ploidy of this cell? What is the n (haploid) number of chromosomes? What is the ploidy of the resulting daughter cells? How many total daughter cells result from this type of cell division? Are there homologous chromosomes in this cell? Are there replicated chromosomes in this cell? Name the filamentous structures along which chromosomes travel (9) 2. List all the unique gametes that an organism with each of the following genotypes could form, assuming crossing over DOES NOT takes place. Be sure to circle each gamete. (6) AB De ab dE EeQqnn XE Y XADXad FF 3. Please tell me the type of point mutation being described (be specific!) and describe the result of that mutation on the amino acid sequence AND polypeptide that is made from the mutated DNA. (6) Mutation Specific type of Mutation Result A “C” replaces a “T” at the second position of a codon A “C” is inserted into the daughter DNA strand A “G” replaces an “A” at the third position of a codon 4. In snakes, color is determined by alleles at two unlinked genes. Gene R determines pigment color with R (red) dominant over r (orange). Gene D then determines pigment deposition, and therefore color presence or absence, with D (red or orange color) dominant over d (colorless). A red snake mates with a colorless snake. Their F1 offspring appear in the ratio of 1 red: 1 orange. Determine the genotypes of parents and offspring, link the phenotypes of offspring to their genotypes, and show all your work. (7) 5. Complete the following chart. Reaction Reactants (substrates) DNA replication 1. DNA molecule 2. Transcription Translation Starch digestion Hydrogen peroxide digestion 1. 2. Ribonucleotides 1. mRNA 2. 1. H2O 2. 2 H2O2 molecules Enzymes or Helper molecules 1. 2. 3. Ligase RNA polymerase (12) Products Two DNA molecules 1. 1. tRNA 2. 1. 1. 1. 1. H2O 2. Maltose and Glucose 2. You find a purple-flowered, tall pea plant. The genes that code for plant height and flower color are unlinked, the allele which produces purple color is completely dominant to the one which produces white, and the allele which produces tall plants is completely dominant to the one which produces short. (8) a. List all the possible genotypes of this purple-flowered, tall plant. b. List the phenotype and genotype of the plant you would cross the purple, tall plant with in order to reveal its genotype. c. Offspring of this cross appear in the following ratios: 1 purple, short: 1 purple, tall. Find the unknown genotype of the parent using a Punnett square, and show your work. 14. An n=3, diploid organism’s genotype is AaBBDd; Draw a normal somatic (body) cell from this organism, placing alleles of the A, B and D genes on their correct, unreplicated chromosomes. (6)