* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells (Stations) part 2 File
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
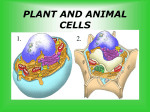
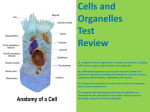
Station 7 30. What is the correct sequence of the level of organizations for plants and animals? A. B. C. D. A. Cells, organs, tissue, organ system, organism Organism, organ, organ system, tissue, cells Cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism Tissue, organ, organism, organ system, cell 31. A student is making a presentation on the level of organization in plants and animals for his science class. He prepares this flowchart to illustrate his presentation. After further study, the student realizes his flowchart is incorrect. Which change should he make to correct the flowchart? A. B. C. D. 33. Which of the following correctly diagrams the level of organization? B. C. Add the phrase cell membrane Move organ system to the beginning Remove tissue and cells Swap organs and cells 32. Use the following picture to identify and organize the correct level of organization D. 34. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? A. B. C. D. Cells, organs, tissue, organ system, organism Organism, organ, organ system, tissue, cells Cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism Tissue, organ, organism, organ system, cell A. B. C. D. They are identical to one another. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus Prokaryotic cells have a nucleus Both cells have a nucleus STATION 8 35. Which of the following best defines organelles? A. B. C. D. 38. Plant and animal cells have structures in common. Which two organelles do plant cells have that animal cells do not have, and what are their functions? Nuclei control the functions of the cell A structure in a cell that has a specific function The smaller organs in a human The part of a cell that does not move or take up space A. 1. Cytoplasm – a gel-like substance containing a large amount of water 2. Cell membrane – stiff covering outside the cell that protects and supports the cell B. 1. Cell wall - stiff covering outside the cell that protects and supports the cell 2. Chloroplast – place where food is produced and chlorophyll is located C. 1. Chloroplast - a gel-like substance containing a large amount of water 2. Cell membrane – outer covering around cell that helps control movement of material into and out of cell D. 1. Cell wall - stiff covering outside the cell that protects and supports the cell 2. Cytoplasm – place where food is produced and chlorophyll is located 36. A student looks through a microscope to compare and contrast an animal and a plant cell. He sees an organelle similar in both cells, as indicated by the arrow. What is the name and function of this organelle? A. B. C. D. 39. Structure Vacuole, which stores waste and food inside the cell Golgi body, which stores and transports proteins Nucleus, which contains the cell’s genetic material Lysosome, which stores enzymes created in the endoplasmic reticulum 37. A student prepared the following list of characteristics about a cellular organelle. • present in animal cells • present in plant cells • helps make energy available to the cell Which of the following cellular structures did the student identify? A. Cell wall B. Chloroplast C. Mitochondrion D. Nucleus Function Vacuole 1. 2. Provides the cell with energy Nucleus Control center of the cell Which of the following correctly completes the table above? A. B. C. D. 1-Stores waste, water, and nutrients, 2- Mitochondria 1- Vacuums water inside the cell, 2- Cytoplasm 1- Provides the cell with structure, 2- Cell wall 1- Uses radiant energy from the sun to make sugar, 2- Chloroplast 40. The nucleus of a cell is the like a human brain becauseA. they both provide energy. B. they both control functions. C. they both remove waste. D. they both provide support. STATION 9 41. Study the diagram of an organelle in an animal cell. 43. Skeleton Structure & Protection Stomach Breaking down food for energy Rectum & Bladder Waste Removal The table above shows organs of the human body and the functions they serve. Similar to a multicellular organism, a cell needs to carry out similar functions. Which organelle is responsible for the function of providing protection and shape to a plant cell? Which of the following is the correct pairing of this organelle and its function? A. Chloroplasts :: produce food B. Mitochondria :: release energy stored in food C. Golgi Apparatus :: processes and packages proteins for storage or for immediate use D. Vacuoles :: convert fats to carbohydrates A. The nucleus B. The cell membrane C. The cell wall D. The vacuole 45. Which process would the energy-releasing organelle in cells 2 and 3 most likely have in the animal cell? 44. A. Cellular control B. Cellular respiration C. Removal of wastes D. Storage of nutrients 46. The cell theory was credited from the work of Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow, which showed three basic facts about cells. The development of the cell theory was possible – When an animal is converting chemical energy to mechanical energy, it produces waste. Likewise, whenever a cell is converting energy, it also produces waste. Which organelles are responsible for converting energy and removing waste? A. B. C. D. The The The The cell wall and nucleus mitochondria and vacuole vacuole and golgi apparatus cell membrane and cytoplasm A. after the microscope was developed and the scientists were able to view cells. B. after cells evolved from new species of plants and animals. C. once it was discovered that plant and animal cells have exactly the same organelles. D. once scientists could distinguish between living and nonliving organisms. STATION 5 47. A 7th grade science student compares and contrasts living organisms with non-living things. Which of the following statements about living organisms and/or non-living things is supported by cell theory? A. All living and non-living things are composed of cells. B. Only non-living things are composed of matter. C. All living things and only living things are composed of cells. D. Cells of living things have different functions from cells of non-living things. 48. A science student looks at hundreds of organism cells under a microscope and reads articles describing cells, their structure, and their functions. What can the student correctly conclude from their investigation that supports cell theory? A. Most cells are not necessary for carrying on life functions in living things. B. All organisms are multicellular. C. When one of an organism’s cells die, the organism dies as well. D. Cell function is similar in all living things. 49. A botanist observes that many plant cells capture the sun’s energy and convert it into food energy which they can use to live. A zoologist observes that animal cells get their energy from carbohydrates and lipids contained in food. Which principle of cell theory is supported by the two scientists’ observations? A. Cells have similar functions, such as obtaining energy from outside sources to sustain life. B. Different types of cells are studied by different types of scientists. C. Animal cells do not perform functions similar to those of plant cells. D. Plant cells need only sunlight to stay alive. 50. Which of these relationships is correctly stated using cell theory? A. Cells in a tiger have similar functions to the tiger itself, such as obtaining energy from outside sources to sustain life. B. Different types of cells in a tiger are studied by different types of scientists. C. Animal cells in a tiger do not perform functions similar to those of plant cells. D. Just like a flower needs sunlight to survive, plant cells in the flower only need sunlight to stay alive.