* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells AP Bio Test Review ANSWERS
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
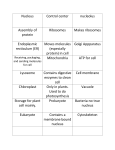
Cells AP Bio Test Review ANSWERS 1. List the first 6 levels of biological organization from smallest to largest 1. Atom, molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ 2. A community of microorganisms living within a shared mass of slime. 2. Biofilm 3. List 2 functions of the nuclear envelope. 3. Separates DNA from activity in cytoplasm & regulates which substances enter & leave the nucleus 4. Prokaryotes lack a _________________. 4. Nucleus 5. What type of cell contains a nucleus? 5. Eukaryotes 6. What limits cell size? 6. Surface area : volume 7. What organisms are prokaryotic? 7. Bacteria 8. What are the functions of a cell nucleus? 8. Controls cell processes, stores DNA, contains info needed to make proteins 9. Define prominent. 9. Important, easily noticed or seen; sticking out in a way that is easily seen or noticed 10. A nucleus is important to cells. The nucleus contains coded instructions for making what? 10. coded instructions for making proteins 11. How does cell size relate to its surface area-tovolume ratio? (smaller cells vs larger cells) 11. The smaller the cell, the higher the SA:V 12. Where is the cytoskeleton found? 12. Between the plasma membrane & nucleus, in the cytoplasm 13. What is the main function of the cell membrane? 13. Regulate the transport of materials in & out of cell 14. Which structure synthesizes polypeptides using coded 14. Ribosomes instructions that come from the nucleus? 15. Which cell structures do not have a membrane? 15. Ribosomes, centrioles, cytoskeletal elements 16. Which 2 organelles help provide cells with energy? 16. Mitochondria & chloroplast 17. Which structures would you expect to find in plant 17. Chloroplasts, cell wall, central vacuole cells but not animal cells? 18. Which organelle would you expect to find in animal 18. Centrioles cells but not plant cells? 19. What is a cell junction? 19. Structure that connects cells together 20. List 3 examples of cell junctions. 20. Plasmodesmata, gap junctions, tight junctions, adhering junctions, desmosomes 21. List adaptations that allow cells to maintain a high surface area to volume ratio. 21. Small cells, membrane extensions (cilia, villi), folded membranes, flat shape 22. Microtubules help build projections from the cell 22. Flagella & cilia surface that aid in cell movement. These structures are known as ______________ & _____________. 23. A cell’s shape and _________ relate to its function. 23. Size 24. If a cell contains a nucleus, it must be a 24. Eukaryote 25. Ribosomes stud the surface of 25. Rough ____________ endoplasmic reticulum. 26. Single-celled organism is called 26. Unicellular 27. Multi-celled organism is called 27. Multicellular 28. What is the function of Golgi Bodies? 28. Processes, sorts, & packages cellular secretions (lipids, enzymes, proteins) for export from the cell. 29. What characteristics do all living organisms share? 29. .Made of cells, have DNA as genetic material that is passed to offspring, they change over generations (populations adapting/evolving), they change (grow, mature, age), engage in processes like homeostasis & metabolism 30. What 4 structures do all cells have in common? 30. Cytoplasm, DNA, cell membrane, ribosomes 31. Summarize the endosymbiotic theory. 32. Explain which intracellular structures make up the endomembrane system and their functions. 33. Compare & contrast prokaryotes & eukaryotes. Know examples of each. 34. Illustrate a plant & animal cell, and know how to identify the different structures.