* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STUDY GUIDE FOR TEST ON CELL STRUCTURE
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
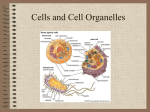
7th GRADE STUDY GUIDE FOR TEST ON CELL STRUCTURE (UNIT 2) Vocabulary: 1) Cell: the smallest unit of structure and function in living things 2) prokaryotic cells: cells with no membrane around nuclear material 3) eukaryotic cells: cells with a nucleus and nuclear membrane 4) organelles: structures within cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells 5) Cell membrane: forms outer boundary of cell; allows materials to move in (food, O 2) and out (waste) of cell 6) Cytoplasm: gel-like material inside membrane 7) Nucleus: largest organelle; directs activities of cell (control center) 8) Chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed of DNA and proteins that condenses to form chromosomes during cell division 9) Chromosomes: threadlike strands of DNA and protein in a cell nucleus that carry genetic information in the form of genes. 10) Nucleolus: small dark structure in the nucleus that makes ribosome parts 11) Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): folded membrane that moves materials around cell (transportation system) 12) Ribosomes: where proteins are made 13) Golgi bodies: stacks of membrane covered sacs that move proteins out of cell 14) Mitochondria: organelles where food molecules are broken down- energy is released (power-houses of cell) 15) Lysosomes: organelles that digest wastes (garbage removal) 16) Vacuoles: fluid filled storage areas in cells (store H2O, food, wastes, etc.); large in plant cell 17) Cell wall: rigid structure that supports/protects plant cell 18) Chloroplasts: organelles where light energy is changed to chemical energy 19) Chlorophyll: green pigment that traps light energy Know: -about the cell parts and the job they perform -be able to identify the parts of a bacteria, plant, and animal cell given a diagram of the cell -the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells -the kingdom that contains prokaryotic cells (Monera or the Bacteria Kingdom) -the kingdoms that contain eukaryotic cells (protist, fungi, plant, animal) -what bacteria cells contain (cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, single chromosome, ribosomes) -how cells differ in size/shape (some nerve cells are a meter long, egg cells are the size of a period on a page) -how the shape of a cell tells us something about the jobs they do (e.g.- nerve cells long with extensions to send messages, plant stem cells are long and hollow to transport food and water, red blood cells are disk shaped to carry oxygen and flexible to move through blood vessels) -that proteins are the building materials of cells -why we stain cells and how cells are stained and slides prepared