* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic D.4 Heart - Cougar science rocks!
Survey
Document related concepts
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
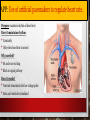
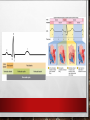
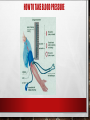
U: Structure of Cardiac muscle cells allows propagation of stimuli through the heart wall Comparison to skeletal muscle: Similarities: striated, long fibers Differences: • Shorter & wider • Y-shaped cells • one nucleus per cell • Intercalated discs = junction between cells • Under INvoluntary control Cardiac cells contract as if one large cell • Y-shaped cells and Intercalated discs allow physical connection • Gap junctions allow electrical connection – (channels of connected cytoplasm between cells) • Both allow rapid movement of ions & a wave of depolarization to pass easily from cell to cell • Both allow synchronization of muscle contraction • Network of cells contract as if it was 1 large cell Identify… • Cardiac muscle fibers • Orange & blue • Mitochondria • Red • One sarcomere • Between narrow dark blue lines • Intercalated disc • Wavy dark blue line U: Signals from the sinoatrial node that cause contraction cannot pass directly from atria to ventricles Cardiac cycle = one complete heart beat Systole = contraction of heart Diastole = relaxation of heart/filling of blood Cardiac Cycle animation The Pacemaker SA node = sinoatrial node = “pacemaker” oCollection of cells that spontaneously initiate action potentials without stimulation by other nerves oGap junctions allow electric charges to flow freely between cells, so spreads rapidly across atrium SA node AV node AV Bundle Purkinje fibers (NOTE: AV bundle a.k.a. Bundle of His) SA node AV node AV bundle Purkinje fibers Pressure changes inside heart U: There is a delay between the arrival and passing on of a stimulus at the atrioventricular node. Delay of ~0.12 s Features of AV node that cause delay: • Smaller fibers • Fewer Na+ channels • Fewer gap junctions • More non-conductive connective tissue U: This delay allows time for atrial systole before the atrioventricular valves close • Delay allows time for atria to empty blood into ventricles before ventricles contract. • Once ventricles contract, AV valves snap shut. • If no delay, AV valves would close too early & not enough blood would go into ventricles! U: Conducting fibres ensure coordinated contraction of the entire ventricle wall Once through AV bundle, signal conducted rapidly to coordinate contraction of ventricles Contraction of ventricles begins at the apex. Features of Purkinje fibers allowing fast signal: • Fewer myofibrils • Bigger diameter • More Na+ channels • Lots of mitochondria and glycogen stores Signal conduction through heart animation NOS: Developments in scientific research followed improvements in apparatus or instrumentation: invention of stethoscope led to improved knowledge of the workings of the heart. Stethoscope = tool for listening to heart & lungs, and to check blood pressure Invented by Rene Laennec, 1816 History of stethoscope First tool allowing for non-invasive investigation of internal anatomy (e.g. abnormal heartbeats) Why was there a need? Before stethoscopes, doctors placed ear directly on chest… • If patient obese, can’t hear heartbeat • Bathing was not social norm… gross! • Female patients… ‘nuf said Evolution of the stethoscope! New Visual Stethoscope records heart sounds for 10 seconds U:Normal heart sounds are caused by AV valves and semilunar valves closing, causing changes in blood flow Normal heart beat = 2 sounds LUB = closing of AV valves DUB = closing of semilunar valves Skill: Measurement & interpretation of heart rate under different conditions Variables that can influence heart rate: Types of exercise Intensity of exercise Recovery from exercise Relaxation Body position Breathing and breath holding Exposure to a cold stimulus Facial immersion in water Ways to take a pulse DBQ p688 Cold Exposure & Heart Rate Answers: 1. 89 BEATS MIN-1 2. 83 - 89 /89 × 100% = 6.7% DECLINE 3. decline is small/data is variable; experiment limited: face or total exposure might have a more profound reduction/greater time of exposure might have an effect; data is inconclusive APP: Use of artificial pacemakers to regulate heart rate. Purpose: maintain rhythm of heart beat How it maintains rhythm: • Constantly • Only when heartbeat is missed Why needed? • SA node not working • Block in signal pathway How it works? • Ventricle stimulated with low voltage pulse • Atria and ventricles stimulated ARTIFICIAL PACEMAKER SKILL: Mapping of cardiac cycle to a normal electrocardiogram (ECG) trace P wave = atrial systole (contract) QRS wave = ventricular systole (contract) T wave = ventricular diastole (relax) Analysis of EKGs: Lengths of intervals between waves Height of R wave Overall pattern compared before/after exercise or different positions of body APP: Use of defibrillation to treat life-threatening cardiac conditions. Ventricle fibrillation = twitching of ventricles due to rapid and chaotic contraction of individual muscle cells Consequence: heart can’t pump any blood, cardiac arrest Defibrillator = device that discharges electrical current to restore normal heart rhythm Note: Can begin with ventricle tachycardia (“v-tach”) = fast heart rhythm APP: Causes & consequences of hypertension & thrombosis Atherosclerosis = hardening of arteries caused by formation of plaques (atheromas) on inside Plaque = debris (fat, cholesterol) Clot = thrombosis = RBCs caught up in the plaque Can lead to hypertension (high BP) Consequences of thrombosis: • • Blockage of blood flow Myocardial infarction (heart attack) Consequences of hypertension: • • • • Narrow & stiff arteries Aneurysm = bulging of weak artery (can burst and cause internal bleeding) Stroke due to blood vessels in brain narrowing, clotting, rupturing, leaking Kidney failure due to damage to arteries leading to kidney & damage to glomerulus Risk factors for thrombosis and hypertension • • • • • • • • • • GENETICS AGING POST-MENOPAUSE (DROP IN ESTROGEN) – ESTROGEN MAY KEEP BLOOD VESSELS FLEXIBLE MALES (LOW ESTROGEN) SMOKING (RAISES BP) HIGH-SALT DIET ALCOHOL STRESS HIGH-SATURATED FAT AND CHOLESTEROL DIET HEIGHT SKILL: Interpretation of systolic & diastolic blood pressure measurements Blood pressure = arterial pressure Ventricular systole/ventricular diastole Normal = 120/80 mm Hg High = 140/90 (only one has to be high) Pre-eclampsia = high bp during pregnancy SKILL: Analysis of epidemiological data relating to the incidence of coronary heart disease Epidemiology = study of spread of disease through a population CHD = coronary heart disease = damage to heart as result of reduced blood supply to heart tissue • Often caused by narrowing & hardening of coronary artery • Groups that may differ in CHD risk: ethnic, gender, age, physical activity, genetics, medical history • ROGER VL, GO, AS, LLOYD-JONES DM, ET AL. HEART DISEASE AND STROKE STATISTICS—2012 UPDATE: A REPORT FROM THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION. CIRCULATION.2012:E2-E220. HOW TO TAKE BLOOD PRESSURE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF CHD • NATIONAL HEALTH AND NUTRITION EXAMINATION SURVEY: 2009–2012.