* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Simon Rasmussen Assistant professor CBS
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
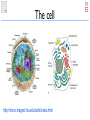
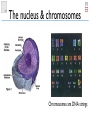
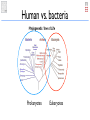
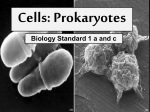
Very short primer on cell biology Simon Rasmussen Assistant professor CBS - DTU The cell http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/index.html The nucleus & chromosomes Chromosomes are DNA strings DNA 4 different bases: A, C, G, T Double stranded, complimentary Pairs together as: A-T and C-G The Central Dogma DNA transcribed into mRNA DNA mRNA translated into protein mRNA proteins are the active units, eg. cell building blocks, enzymes, ... Ribosome Protein Information never goes the other way (except for some virus) A gene Gene: Stretch of DNA that gets transcribed into mRNA Human vs. bacteria Human vs. bacteria Prokaryotes Human vs. bacteria Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Prokaryotes: Single cells, no nucleus DNA spread out in the cell Eukaryotes: Multi-cellular, DNA inside nucleus Sequencing • Genome: All DNA on chromosomes inside the cell • Sequencing is trying to read the bases of the genome Polymerase Chain Reaction • • More is often needed for sequencing • DNA can be amplified using Polymerase Chain Reaction DNA is often found in very low amounts (eg. 1 ug) • Use DNA polymerase (enzyme) and primers (small pieces of DNA that bind to region of interest) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HMC7c2T8fVk&feature=related