* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids ATP – The
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
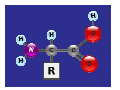
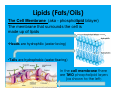
Today’s Agenda Today’s Topic: Friday November 9th, 2012 Chemistry of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids ATP – The Cells Fuel ive: t c e j b O s ’ y a d o T he t e r a Wh a t i on s t c a e r al c i e m d e i h s c n i e plac e k a t that l? l e c e h t Today’s Science Starter Take out Enzyme Notes, Lab sheet and Study Guide Today you need pen/pencil/highlighter Tonight’s Homework Test on Wednesday 11/14: check your notes and vocab daily on Quia page Organize the information you have and can collect in order to study efficiently. REMEMBER: Just looking at the information on each sheet is NOT studying. Develop study strategies! A Cell usually contains lipids carbohydrates oils and fats which are made of proteins DNA which are made of which is a which may be amino acids sugars enzymes nucleic acid which is made of nucleotides enzymes Properties of Enzymes: A Study of Catalase Review: Enzymes are proteins. -specialized reactions proteins that speed up chemical They aid in: 1. digestion - the breaking down of protein, carbohydrates and fats 2. synthesis of complex substances – the joining together to make macromolecules 3. hydrolysis of complex substances – the breaking apart of complex molecules into simpler molecules Amino Acids Amino acids are important organic compounds made from amine (NH2) and carboxylic acid (COOH),along with a side-chain specific to each amino acid.] The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Proteins are macromolecules made from amino acids (the subunit) binding together. About 500 amino acids are known. http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Fil e:Main_protein_structure_levels_en.svg&p age=1 How does it work? DNA is made up of the four nucleotides adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T), which are arranged in a certain order along the strand. An example might be: ACGGTC. Each three-letter combination codes for a certain amino acid. In this case, ACG would code for one amino acid, and GTC another. Then those amino acids are put together to form proteins, which are used to build the structure of a cell and fuel all the cell’s functions. These three-letter combos are called codons. !Nucleotides make up codons; codons code for amino acids; amino acids are put together into proteins; proteins make up cells; cells make up organisms. And thus DNA is the basis of life. Jonathan Coulton sings a fun song about it. enzymes Simple Sugar Molecules • 1-3 molecules long • Simple sugar molecules include: " Glucose (C6H12O6) " Fructose - Seen as part of high fructose corn syrup " Lactose - “Milk Sugar” - Made of glucose and galactose (another simple sugar) Complex Sugar Molecules • Four or more sugar molecules long • Complex sugar molecule includes: " Amylose (5X glucose) • Plants store glucose in the form of amylose (aka starch) Complex Sugar Molecules • After Chloroplasts produce individual molecules of glucose, the glucoses are linked to form a complex sugar molecule (aka starch or amylose) • This starch is either stored in chloroplasts or broken down and exported to be used by the mitochondria Chloroplast chloroplast Mitochondria Simple sugar Lipids (Fats/Oils) Use in the Body •Stores energy (more than carbohydrates) •Protects AND insulates your internal organs •Helps nerve cells with transmission of signals Food Sources •Plant Oils – olive oil, canola oil, vegetable oil •Animal Fats – cream, butter, fatty meats Lipids (Fats/Oils) The Cell Membrane (aka - phospholipid bilayer) The membrane that surrounds the cell is made up of lipids •Heads are hydrophilic (water loving) •Tails are hydrophobic (water fearing) In the cell membrane there are TWO phospholipid layers (as shown to the left) Lipids (Fats) Which part of the phospholipid is the fat? The head or the tale?