* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7 Grade: Ch. 10 STUDY GUIDE KEY
Survey
Document related concepts
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
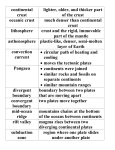
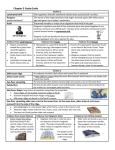
Name: ____________________________________ Class: _______________ Date: _____________ 7th Grade: Ch. 10 STUDY GUIDE KEY Write out all questions and their answers in your journal. Take as many pages as you need – don’t crowd your work! The test is: ___________________ 1. What was Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift? The continents were once joined together in a single landmass 2. What is Pangaea? Pangaea is the name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years ago 3. What is a fossil? Any trace of an ancient organism that has been preserved in rock 4. What technology did scientists use in the mid-1900’s to map the mid-ocean ridge? Sonar 5. Where does molten material rise from the mantle when it erupts? Along Mid-ocean Ridges 6. Old oceanic crust is more ____________ than new oceanic crust because it is cool. Dense 7. What do most geologists think causes the movements of Earth’s plates? Convection currents in the mantle 8. What is the theory of Plate Tectonics? Plate Tectonics is the theory that states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant slow motion. 9. When two plate slip past each other, moving in opposite directions, what boundary is present? Transform Boundary 10. A collision between two pieces of continental crust at converging boundaries produces: Mountain ranges 11. What does the hypothesis of Continental Drift propose? All the continents were once joined in a single landmass that has since drifted apart. 12. What occurs where the oceanic crust bends down toward the mantle at a deep-ocean trench? Subduction 13. These are contained in the lithosphere which float above the asthenosphere? Plates 14. An ocean will _____________ if subduction occurs faster than oceanic crust can be created. Shrink! 15. Younger oceanic crust can be found near the _______________. Mid-ocean Ridge 16. Wegener provided evidence to support his theory of Continental Drift 17. How do plates move at a transform boundary? Two plates slip past each other, moving in opposite directions 18. What are the three types of evidence Wegener provided? Land features; fossils; climate 19. Why didn’t most geologists of Wegener’s time accept his idea of the drifting continents? Wegener couldn’t explain how continents actually moved. 20. What does the term, boundary, mean? Where one place ends and another begins 21. A continent’s climate gets (warmer/colder) as it moves toward the equator. 22. What feature forms the longest mountain ranges on Earth? The mid-ocean ridges 23. Where does subduction occur? At Deep Ocean trenches 24. Which process adds more crust to the ocean floor? Sea-floor spreading 25. What two processes change the size and shape of the oceans? Both subduction and sea-floor spreading 26. What does the prefix, “con-“ mean? Together 27. Older rock samples can be found where? Far from mid-ocean ridges 28. Sea floor spreading occurs at Mid-ocean ridges 29. What are transform boundaries? Where plates slide past each other 30. What currents drive Earth’s plate movements? Convection 31. What is the motion of Earth’s plates? Slow and Constant 32. Which land feature forms at convergent boundaries? Mountain range 33. What transform boundary is found in California? San Andreas Fault 34. Which theory describes the motion of and force driving Earth’s plates? Plate tectonics 35. What boundaries are where plates move apart? Divergent boundaries 36. Draw a transform boundary, a convergent boundary, and a convergent boundary. 37. Identify the three forms of evidence that support scientists ideas of sea floor spreading. Molten material; magnetic stripes; drilling samples 38. Be able to identify from a drawing what is happening at a deep-ocean trench! BONUS! Write this 5 times: Packers will beat the Bears!