* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitosis - TeacherWeb
Survey
Document related concepts
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
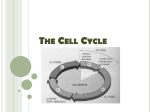
Mrs. Crouch Biology 1 Honors the Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle & Mitosis •A period of time from the beginning of one cell division to the beginning of the next cell division. G1 Phase M Phase S Phase •Divided into 4 phases (G1, S, G2, and M) G2 Phase Interphase Cell Cycle Mitosis G1 Phase •Growth & activity •Cell double in size •Number of ribosomes & mitochondria double S Phase •Chromosome replication •DNA molecules duplicate G2 Phase •Final preparation for division •Spindle fibers assemble Mitosis •Actual cell division • The process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells undergo a similar process called binary fission 4 Phases of Mitosis Chromosome Chromosome • has 2 coiled chromatids, joined at the centromere Chromatid • Single strand of a chromosome • Found in identical pairs • Called “sister chromatids” Centromere • Part of the chromosome where the chromatids are attached Prophase •Longest phase (60%) Chromatid Centromere Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase •Chromosomes come together and form thick thread like structures •Centrioles separate (in animal cells only) •Spindle fibers grow from the centrioles Draw Me Rancho High School 1 Mrs. Crouch Biology 1 Honors Metaphase Anaphase •Shortest phase •Centromeres holding the chromatids split •Chromosomes are completely attached to spindle fibers •Microtubules pull the chromatids apart •Chromosomes line up in the center of the cell •Chromosomes (single stranded) are now at two separate ends Cytokinesis After cytokinesis, the daughter cells return to interphase Telophase •Spindle fiber begins to break apart •Chromosomes at each end of the cell, start to spread out •Nuclear membranes form around each cluster of chromosomes - Two distinct nuclei are formed within the cell Mitosis (Onion Cell) •Cytoplasm and it’s contents divide into 2 daughter cells •Each daughter cell receives 1 nucleus and half of the cytoplasm & organelles Cell Cycle and Cell Division Facts Questions? Comments? Mouse Cell - completes the cell cycle in 22 hours Bean Cell - completes the cell cycle in 19 hours Adult Human -Around 2 trillion cell divisions occur in a 24 hour period * This = 25 million cell divisions per second! Rancho High School 2