* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
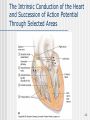
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
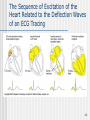
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
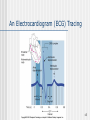
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
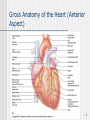
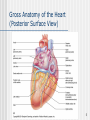
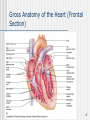
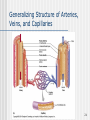
The Heart 1 Description of the Heart (Part 1) Heart location Ventral cavity – Thoracic cavity – Mediastinal cavity – Pericardial cavity 2/3 shifted left Extends from rib 2 to 5th intercostal space Apex • Left ventricle • Points toward left hip Base • Upper posterior surface • Predominantly left atrium Sternocostal surface Diaphragmatic surface Individual’s heart is about the size of the person’s closed fist 2 Description of the Heart (Part 2) Pericardial Sac Fibrous pericardium Serous pericardium • Parietal • Visceral • Pericardial cavity Cardiac Wall Epicardium – Visceral pericardium Myocardium – Muscle layer Endocardium – Lining Clinical Applications CPR Cardiac tamponade Pericarditis Myocarditis Endocarditis • Chambers • Valves 3 Gross Anatomy of the Heart (Anterior Aspect) 4 Gross Anatomy of the Heart (Posterior Surface View) 5 Description of the Heart (Part 3) Cardiac Chambers • Left • Receives oxygen enriched blood from lungs Atria • Thin walls • Pectinate muscle • Separated by • Interatrial septum • Fossa (foramen) ovalis • Right • Receives oxygen depleted blood from body • Lowest blood pressure in body Ventricles • Thick walls • Trabeculae carnae • Separated by – Interventricular septum • Right • Receives blood from R. Atrium 6 Description of the Heart (Part 4) • Pumps blood to lungs • Left • Receives blood from L. atrium • Pumps blood to body • Highest blood pressure Cardiac Valves Structure • Cusp • Endocardium • Dense connective tissue Function • Prevent reverse flow Location & surface projection • Tricuspid • R. atrioventricular valve • R./L. 5th intercostal space, near sternum • Pulmonary semilunar • R. ventricle pulmonary trunk • L., 2nd intercostal space near sternum • Chordae tendinae • Papillary muscle 7 Gross Anatomy of the Heart (Frontal Section) 8 Description of the Heart (Part 5) • Bicuspid (mitral) • L. atrioventricular • L., 5th intercostal space in midclavicular line • Aortic semilunar • L. ventricle aorta • R., 2nd intercostal space, near sternum Great vessels of the Heart 9 Description of the Heart (Part 6) Inferior vena cava (IVC) Coronary sinus Superior vena cava (SVC) Pulmonary trunk – Right ventricle Pulmonary veins – Left atrium Aorta – Left ventricle 10 Cardiac Conduction System (Part 1) Specialized myocardial cells Autorhythmic Pacemaker Conduction system Pacemaker cells set up basic rhythm of contractions Conduction system coordinates contraction of myocardial fibers Conduction system components Sinoatrial (SA) node • In R. atrium near SVC opening • Primary pacemaker • Impulse transmits to AV node • Maintains rhythm of 60-100 bpm Atrioentricular (AV) node • In interatrial septum • Secondary pacemaker • Impulse transmits to AV bundle 11 The Intrinsic Conduction of the Heart and Succession of Action Potential Through Selected Areas 12 Cardiac Conduction System (Part 2) • Sets basic rhythm if SA node is not functioning • Maintains rhythm of 40-50 Atrioventricular bundle (Bundle of His) • Electrically links atria to ventricles • In septa • Impulse transmits to bundle branches • Maintains rhythm of 20-40 R.&L. bundle branches In interventricular septum Impulses transmit to myoconduction fibers Conduction myofibers (Pukinje fibers) • In ventricular walls • Impulses transmit to ventricular walls Clinical applications Artificial pacemakers Bundle branch block • Complete • Right • Left 13 The Sequence of Excitation of the Heart Related to the Deflection Waves of an ECG Tracing 14 An Electrocardiogram (ECG) Tracing 15 Summary of Events Occurring in the Heart During the Cardiac Cycle 16 Cardiac Cycle (Part 1) Events associated with one heart beat – Lasts about 0.8 sec R. & L. sides Acts simultaneously Develop different pressures Expel the same volume Chambers fill passively Atria contract while ventricles relax Ventricles contract while atria relax Systole – Contraction phase Asystole – Relaxation phase Phases Relaxation (Quiescent) period • At end of heart beat – lasts about 0.4 sec • All 4 chambers relaxed – Pressure drops backflow of blood • Trapped by closing of semilunar cusps of vavles – Dicrotic notch 17 Cardiac Cycle (Part 2) • All 4 valves closed – Isovolumetric relaxation • Ventricular pressure < atrial pressure – AV valves open Ventricular filling • • • • Rapid ventricular filling – Passive Diastasis Atrial systole – Final 30mL – 0.1 sec End diastolic volume (EDV) – about 130 mL 18 Cardiac Cycle (Part 3) Ventricular systole • • • • • • • • AV valves shut – 1st heart sound All 4 valves closed – Isovolumetric contraction Ventricular pressure rises Semilunar valves open Ventricular ejection – 0.5 sec Semilunar valves close – 2nd heart sound Systole begins End systolic volume (ESV) – 60 mL Stroke volume = EDV –ESV Cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate 19 Factors Involved in Regulation of Cardiac Output 20 Generalizing Structure of Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries 21