* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download My Cell Division Notes [PDF Document]
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
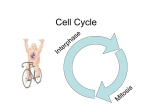
Cell Division | Topic Notes Cell continuity refers to living cells arising from living cells of the same type. Chromosomes are tightly coiled and highly organised structures of D.N.A and protein. (referred to as chromatin when cell isn’t dividing) Genes are short regions of chromosomes that contain a code for the production of a protein. Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes. (humans have 23 pairs) Haploid cells have one set of chromosomes (sperm and egg, i.e.23) Diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes (all other body cells, i.e. 46) Interphase is a long period of the cell cycle in which the cell spends most of its life carrying out everyday activities. Mitosis is nuclear division in which the number of chromosomes in the daughter nuclei is the same as the parent nucleus. its stages include: 1. Prophase: chromatin-chromosomes, chromosomes attach at centromeres, nuclear membrane begins to dissolve and centrioles produce spindle fibres. 2. Metaphase: chromosomes line up along equator and spindle fibres attach to centromeres. 3. Anaphase: spindle fibres pull duplicated chromosomes apart at centromere to either pole. 4. Telophase: nuclear membranes begin to reform and spindle fibres dissolve. A cleavage furrow forms in animal cells while in plants a cell plate forms. Mitosis is used in single celled organisms for reproduction. Mitosis is used in multicellular organisms for growth and repair. Cancer is a group of disorders in which the cells lose control over the rate of mitosis and cell division. There are two types : 1. Benign-forms a tumour and stays in one position. 2. Malignant-have the ability to leave tumour. (more serious) Causes of cancer include UV light, cigarette smoke and radon gas. 1 Cancer can be treated by surgery, radiotherapy or chemotherapy. Meiosis is a type of cell division in which four daughter cells are produced, each containing half the nr. Of chromosomes as the parent cell. Meiosis is important in multicellular organisms for sexual reproduction to occur, it doesn’t occur in single celled organisms. 2

















![MITOSIS WORKSHEET - New Page 1 [bs079.k12.sd.us]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014668413_1-30813973b0cb9de17ced950a5cb16263-150x150.png)