* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Second test Spr 02
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Mitogen-activated protein kinase wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
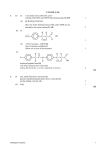
Biochemistry 694:301 Second Exam, Dr. Deis Wednesday Mar. 13, 2002 Name___________________________ Last 5 digits of I.D. Num ___________ Row Letter ____ Seat Number ______ This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth two points. Answer the Part I questions on this sheet, below. Answer the Part II questions on the question pages. Please use BLOCK CAPITAL letters like this --- A, B, C, D, E. Not lowercase! 1. ______ 10. ______ 18. ______ 2. ______ 11. ______ 19. ______ 3. ______ 12. ______ 20. ______ 4. ______ 13. ______ 21. ______ 5. ______ 14. ______ 22. ______ 6. ______ 15. ______ 23. ______ 7. ______ 16. ______ 24. ______ 8. ______ 17. ______ 25. ______ 9. ______ GRADE: Part I Total _______ Part II: II-1 II-2 II-3 II-4 II-5 _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ Part II Total _______ Total, I & II _______ 694:301 Second Exam, page 2 Name ________________________ 1. Hemoglobin's binding is affected by a variety of heterotropic effects. Which of the following is not a negative allosteric modulator? A. H+ D. 2,3 BPG B. CO2 E. none of the above C. oxygen 2. If a solution of Hemoglobin is oxygenated to half its capacity, what would you expect to find in the solution? A. only Hb(O2)2 D. mono, di, and trioxy Hb B. half Hb, half Hb(O2)4 E. none of the above C. equal amounts of Hb, Hb(O2)2, and Hb(O2)4 3. The heme group is positioned in the heme pocket by Fe binding to a residue of A. histidine D. histamine B. alanine E. glutamine C. serine 4. Where does 2,3 Bisphosphoglycerate bind to the Hemoglobin molecule? A. it binds to the heme iron D. at the opening of heme pocket B. to the COOH end of alpha chain E. at the center of the tetramer C. The E helices 5. The 3-epimer of D-Glucose would be A. Fructose D. Allose B. Galactose E. Cellobiose C. Mannose 6. Lab scientists have synthesized a form of Maltose, with an alpha 1 – alpha 1 glycoside instead of the normal alpha 1-4 connection. Is this a reducing sugar? A. yes B. no 7.* Identify the "chair" structure at right: A. α-D-mannose D. β-D-galactose B. β-D-mannose E. α-D-glucose C. α-D-galactose F. β-D-glucose 8. Milk sugar, or Lactose, contains what sort of glycosidic linkage? A. α 1-3 D. β 1-4 B. β 1-3 E. α 1-6 C. α 1-4 F. β 1-6 9. The structure of sphingosine (with nothing attached to it) does NOT include what? A. 18 carbons D. one amino group B. 2 hydroxyls E. one double bond C. 1 carboxyl group 694:301 Second Exam, page 3 10. Membranes are NOT generally A. asymmetrical B. electrically polarized C. made of lipids and proteins Name ________________________ D. covalent assemblies E. bilayers 11. Which would have a higher melting point? A. a saturated fat like Tristearin (no d.b.) B. an unsaturated fat like Triolein (one double bond) C. there's no way to tell 12.* The polar lipid shown below is A. phosphatidyl serine B. phosphatidyl choline C. phosphatidyl ethanolamine D. phosphatidyl inositol E. none of the above 13. Potassium can not pass through the voltage gated Sodium Channel because A. inactivation prevents it D. K+ is too large B. too much Sodium gets in way E. none of the above C. K+ is too positive 14. The Acetylcholine Receptor is composed of how many subunits? A. 4 D. 8 B. 5 E. 12 C. 6 15. The Multidrug Resistance Protein (MDR) A. pumps out small molecules B. is an ABC transporter C. has some homology with CFTR, the Cystic Fibrosis Transmem. Reg. D. all of the above 16. Acetylcholinesterase has a turnover number (k2) of about A. a billion per second D. 250 per minute B. 25,000 per second E. none of the above C. 250 per second 17. In "standard" conditions, [ATP] = 1 Molar, [ADP] = 1 Molar, and [AMP] = 1 Molar. What's the value of Atkinson's Energy Charge? A. 1.0 D. 0.5 B. 0.9 E. 0.33 C. 0.67 F. - 1.0 18. Krebs' diagram of the three stages of Catabolism included the Citric Acid Cycle as A. Stage I D. Stage IV B. Stage II E. none of the above C. Stage III 694:301 Second Exam, page 4 Name ________________________ 19. What factors explain the high energy of ATP compared with a sugar phosphate? Choose two answers. A. Glycosides D. Electron transport B. Entropy E. Resonance Stabilization C. Charge Repulsion 20. One of the enzymes of Fatty Acid Synthesis is named 2,4 Dienoyl CoA Reductase. Based solely on your knowledge of cofactors and how they work, you should be able to predict that the cofactor for this enzyme is: A. FADH2 D. CoASH B. NADPH E. Thiamine Pyrophosphate C. NADH 21. How many Calcium ions (maximum) can Calmodulin bind? A. 2 D. 6 B. 3 E. 12 C. 4 22. One of the second messengers in Protein Kinase C activation is strongly hydrophobic. It is often known by its abbreviation A. PIP2 D. SRO B. CPU E. DAG C. IP3 23. Protein Kinase A phosphorylates enzymes on what kind of residue? A. Tyr D. Ala B. Ser E. Cys C. His 24. Which was described in a handout as "stupid"? (this question counts) A. Lemur D. Chambered Nautilus B. Octopus E. Fish C. Number Five 25. After this test I will A. laugh B. cry C. drink D. watch Sponge Bob E. cannot tell from data provided 694:301 Second Exam, page 5 PART II 1.* Name ________________________ Answer these questions here on the question pages. a. On the axes provided, draw the loading curves for hemoglobin and myoglobin and label which is which. Indicate partial pressure in torr and show where P50 occurs for each curve. (4) b. Sketch the heme group or a tetrapyrrole ring (2) c. The beta chain of HbA starts with the amino acid sequence VHLTPEEK. How is this changed in HbS? What goes wrong, on the molecular level, during a sickling attack? Describe the effects of the disease as shown in class. (4) 694:301 Second Exam, page 6 2. Name ________________________ a. Draw the disaccharide D-mannopyranosyl α1-4 β D-xylulofuranose in the Haworth projection. For partial credit just draw D-Mannose and D-Xylulose in the Fischer projection. (4) b. Draw the alpha and beta anomers of D-Fructopyranose c. Draw Cholesterol d. What's this and where is it found? (2) (2) * (2) 694:301 Second Exam, page 7 3. Name ________________________ Give specific answers to each question: a1. Where is Acetylcholinesterase located? a2. Why is it such a fast-acting enzyme? a3. What happens to an animal exposed to an inhibitor of ACHase. (2) (2) (2) b1. How do you identify Facilitated Diffusion? (What properties would you look for?) (2) b2. (2) Is a Sodium Channel an example? How about the Calcium pump? 694:301 Second Exam, page 8 4.* Name ________________________ a. What cofactors are represented below? b. A -> C -> (4) B B ∆Go' = +5 kcal/mol ∆Go' = +7 kcal/mol What is the standard free energy change for A -> C? Show work and circle answer. (4) c. Fill in the cofactors where needed: (2) COOH CH2 CH2 COOH --> COOH CH || ---> CH COOH COOH HO --- C CH2 ---> COOH COOH O=C CH2 COOH 694:301 Second Exam, page 9 5. Name ________________________ a. How does epinephrine stimulate production of cyclic AMP in liver cells? Diagram the process and explain briefly. What form of Protein Kinase is activated by cyclic AMP? (4) b. (4) Give 4 examples of (different) processes mediated by 7TM receptors ______________________ _______________________ ______________________ _______________________ c. How do Calcium and other activators allow Protein Kinase C to become active? A sketch or diagram would be very helpful in explaining this. (2)