* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Physiology Unit 3A: Endocrine System
Survey
Document related concepts
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
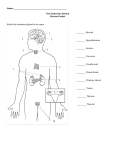
Human Physiology Unit 3A: Endocrine System Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Paige Stieneke BIOL 256 Dr. Karri Haen March 3 and 4, 2013 _____________ Glands: secrete hormones into extracellular space. They travel through the _______________. Hormones bind to __________ on target cells, which ultimately produces an effect. Chemical Classification of Hormones Class Receptors Examples Steroids does not need a receptor, can directly enter the cell/nucleus Estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, aldosterone Peptides Insulin, glucagon, prolactin, ACTH, gastrin, PTH Adrenaline, thyroxine Biogenic Amines cAMP Second Messenger System 1. ______________ (1st Messenger) binds to a receptor, which then activates a ______________ 2. G protein activates _____________________ (an enzyme) 3. Adenylate cyclase generates ________ (2nd Messenger) from ATP 4. cAMP activates protein kinases, which adds ___________ to enzymes, activating or inactivating them Which hormones use the cAMP Messenger System? Phosphatidylinositol System (aka PIP-Calcium Second Messenger System) 1. ____________ (1st Messenger) binds to a receptor, which then activates a _______________ 2. G protein activates ________________ (an enzyme) 3. Phospholipase splits phospholipid PIP2 into TWO different kinds of 2nd Messengers: a. _____ activates protein kinases b. _____ triggers release of Ca2+ stores i. ______ (3rd Messenger) alters cellular responses Which hormones use the PIP-Calcium System? Tyrosine-Kinase System 1. __________ (1st Messenger) binds to a receptor, which activates ____________________ 2. Tyrosine Kinase (TK) _______________ proteins Ex: Insulin binds TK to allow glucose to be taken into the cell, which lowers blood sugar levels Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu Target Cell Activation (Up-regulation, Down-regulation) is where target cells form more receptors in response to a hormone, while (Up-regulation, Down-regulation) is where target cells lose receptors in response to a hormone Hormone Interactions 1. ______________ Effect: 2 hormones required to activate cell, one hormone produces NO effect 2. ______________ Effect: 2+ hormones work together to produce effect, works in an additive way 3. ______________ Effect: 1 hormone counteracts the other hormone’s effects Hormonal Stimulation a. Humoral: b. Hormonal: c. Neural Stimulation: Pituitary-Hypothalamus Relationship 1. Which part in the brain is known as the “master” gland? 2. True or False: the anterior pituitary is glandular tissue, but the posterior pituitary is neural (NOT glandular) tissue 3. Which part of the pituitary gland stores and releases hormones from the hypothalamus? 4. Which part of the pituitary gland synthesizes and releases its own hormones? 5. How does the hypothalamus control hormone release? Thyroid Gland Surrounds the trachea Parathyroid Gland: 4 pea-sized glands on the thyroid gland Controls the __________________________ (BMR), or the average amount of energy expended at rest Review thyroid diseases: Goiter (bulge in throat), Grave’s Disease (eyes pop out), and Cretinism (mental retardation in children) Adrenal Glands Paired, superior to the kidneys ___________________: Out layers of the adrenal glands ___________________: Inner layers of the adrenal glands, nervous tissue acts as part of the SNS Review Cushing’s Syndrome and Addison’s Disease Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu Endocrine Gland Hormone produced Growth Hormone (GH) Anterior Pituitary Define tropic: Tropic Regulation from Hypothalamus: 1. GHRH 2. GHIH Target Organs a. Bone b. Skeletal muscle c. Adipose tissue d. Liver Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Target cells Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Adrenal cortex (zona fasciculata) Effects on Targets a. b. c. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Males: Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Females: a. b. Not tropic c. Posterior Pituitary Prolactin (PRL) Mammary glands Oxytocin Smooth muscle contraction: a. b. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Thyroid Gland Thyroid Hormone All cells in the body Calcitonin Parathyroid gland Increase ____ and heat production a. __________ osteoclast activity b. __________ calcium uptake in bone Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Kidneys and bone a. ___________ osteoclasts to break down bone b. ________ blood levels of calcium Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu Endocrine Gland Hormone produced Mineralcorticoids (Aldosterone) Target Organs Zona fasciculata Glucocorticoids (Cortisol) Body a. Resist ___________ b. Keep blood sugar constant c. Maintain blood volume and prevent water shift into tissue Zona reticularis Gonadocorticoids (Androgens) Body a. Onset of ____________ b. Appearance of secondary sex characteristics Adrenal medulla Epinephrine and Norepinephrine Body Pancreas Glucagon (Alpha) Adrenal Cortex Zona glomerulosa Effects on Targets a. b. a. ___________________: breakdown glycogen into glucose b. ___________________: synthesis of glucose “Fasting hormone” c. Insulin (Beta) Body “Fed hormone” Somatostatin (Delta) Pancreatic Polypeptide (F cells) Regulates release of pancreatic digestive enzymes Female gonads Estrogens and Progesterone a. Maturation of reproductive organs b. Appearance of secondary sex characteristics Male gonads Testosterone a. Maturation of reproductive organs b. Appearance of secondary sex characteristics c. Pineal Gland Thymus Melatonin Thymopoeitin and Thymosin Body Aids in development of T lymphocytes of the immune system Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu