* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 9
Survey
Document related concepts
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Collatz conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
P-adic number wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
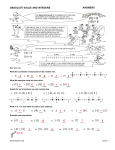
Unit 9 Rational Numbers and the Coordinate Plane Lesson 9-1 Negative Numbers in the Real World Rational Numbers: any number positive or negative that can be written as a fraction. Opposite: numbers that are the same distance from zero on a number line, but in opposite directions. Positive Numbers: to the right or above zero. Negative Numbers: to the left or below zero. Deposit: to put in or add to. Withdraw or Withdrawal: to take out, back away, or subtract from. Integers: all positive and negative whole numbers or rational numbers and zero. Origin: zero is known as origin. It’s the center point for all positive and negative numbers. Origin Lesson 9-2 Integers and the Number Line Value decreases left of zero Value increases right of zero Lesson 9-3 Compare and Order Integers Absolute Value: is the distance an integer is from zero. Represented by brackets │ │. *All absolute values are positive. Examples: │3│= 3 │-15│= 15 Comparing Integers How to: 1. Negative integers are always ‹ -4 0 › ‹ less than positive integers and zero. Examples: 7 │-5│ 3 (5) 2. Small negative integers are greater than -7 ‹ -1 ‹ 10 › bigger negative integers. Examples: -3 › -15 Ordering Integers How to: When ordering integers, pay attention to the signs and the order wanted. Least to greatest or greatest to least. Examples: -8, 24, -15, 0, 1 Ordered least to greatest -15, -8, 0, 1, 24 7, -9, 1, 9, -3, -7 Ordered greatest to least 9, 7, 1, -3, -7, -9 Lesson 9-4 Integers and the Coordinate Plane Quadrant: Coordinate Plane is divided into 4 parts called quadrants. Labeled with Roman Numerals I, II, III, and IV x-axis: The horizontal number line. Always read this axis FIRST. y-axis: The vertical number line. Read this axis SECOND. Origin: is zero on the number line. Ordered pairs: the two numbers (x, y) placed on the coordinate plane. X ,Y Q II Quadrant I (- +) A (3, 6) B (6, 0) C (-1, 6) D (0, -3) E (5, -2) F (-4, 0) G (-3, -4) (+ +) •C •A •F •B •E •D •G Q IV QIII (+ -) (- -) Lesson 9-5 Rational Numbers on the Number Line What to look for: How is the number line divided? Is it divided into quarters, thirds, tenths, halves, wholes, etc..? Look how the number line is labeled. Example: fractions, decimals, odds, or evens. -2 1.75 1.5 1.25 -1 -.75 -.5 -.25 0 .25 .5 .75 1 │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ -1 ¾ -1 ½ -1 ¼ -1 -¾ -½ -¼ 0 ¼ ½ ¾ -2 1.25 1.5 │ │ │ 1 1¼ 1½ 1.75 │ 1¾ Remember what opposite means! Write the opposite of: -2/3 → 2/3 1 ¼ → -1 ¼ Simplifying Rational Numbers -(-1 2/3) = 1 2/3 -(3/4) = -3/4 A negative sign outside a parenthesis means to find the opposite of what is inside the parenthesis. The answer does NOT need parenthesis! Lesson 9-6 Compare and Order Rational Numbers Note: Review Lesson 9-3, before continuing on with this lesson. Working with negative numbers, the closer to zero, the greater the value. Watch for │ │absolute value brackets, and –( ) negative signs outside the parenthesis. Examples: The answers are shown below each example. ≥ ›3 │-5│ 3 5 │-.5│___ │ .5 › 2 5 │ 1 1 4 │- │___ │- │ 2 1 .4 › 2 1 │-.5│___ │- │ 4 .5 4 ‹ 5 .8 Lesson 9-7 Rational Numbers and the Coordinate Plane Reflected Point: The mirror image across an axis. 1.To find the distance between two points on a number line, subtract. A ( 1 1 , ) 2 2 1 1 B (2 , 2 2 1 C ( 2, 3) D (2 1 , 2 Distance between point A and C ) 1 3 – . Subtract the y-coordinates 2 for vertical distance. = 2 3) 1 2 units. Distance between point A and B 2 1 2 1 - . Subtract the x-coordinates 2 for horizontal distance. = 2 units 2. Reflecting across x-axis or y-axis. a. Across x-axis; the x-coordinate stays the same, and the y-coordinate goes opposite. b. Across y-axis; the y-coordinate stays the same, and the x-coordinate goes opposite. Reflect across x-axis A (4,3) to (4, -3) Reflect across y-axis A (4, 3) to (-4, 3) B (-5, -4) to (-5, 4) B (-5, -4) to (-5, -4)