* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key Study Guide Unit 7 Structure and Function of
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
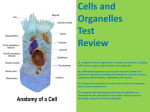
Key Study Guide Unit 7 Structure and Function of Cells 7.12C 7.12C: Recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. 1. List the levels of organization from the least complex “cell” to the most complex “ecosystem”. Use your Science Starter notes “Biological Organization”. The levels of organization from the least complex “cell” to the most complex “ecosystem” are: cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organisms, population, community, and ecosystem. 2. In the levels of organization, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and organism, which structure is the least complex? The cell is the least complex structure in the levels of organization. 3. Thinking of the levels of organization, cell-tissue-organ-organ system: Which is the correct term used to describe a group of body parts working together to perform a specific function? An organ system is the correct term used to describe a group of body parts working together to perform a specific function. 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole. 1. List the structures “organelles” that are only found in plant cells. The organelles that are only found in plant cells are large vacuole, cell wall, and chloroplasts. 2. What is the difference between a eukaryote and a prokaryote? The difference between a eukaryote and a prokaryote is that a eukaryote has a nucleus and prokaryotes do not. 3. In eukaryotes, where is the genetic material for the cell located? The genetic material in eukaryotes is found in the nucleus of the cell. Refer to the images/structure & function of cell organelles we completed in class using the computers to answer questions 4-7. 4. What is the function of the chloroplast in plants? The function of chloroplast in plants is to use energy from sunlight to make sugar/glucose which is food for the plant. 5. How are chloroplast in plant cells and mitochondrion in animal cells similar? Chloroplast in plant cells and mitochondrion in animal cells are similar because both are the energy factories for the cells. 6. If you were looking at an image of two different cells with all the organelles labeled, how would you determine which cell was a plant cell? I could determine a plant cell from an animal cell because plant cells only have cell walls, chloroplast, and a large vacuole. 7. What structure in a cell allows waste to exit/leave the cell? The cell membrane is the structure in cells that allows waste to leave the cell. 8. Draw a picture using the following items to represent organelles in a cell: large rectangular clear plastic container=cell wall, gelatin=cytoplasm, green M&Ms=chloroplast, red licorice=endoplasmic reticulum, several beans=mitochondrion, one large inflated balloon=vacuole and an avocado seed=nucleus. Identify the item that you are using to represent the correct organelle. What type of cell does this represent? This represents a plant cell. 7.12E: Compare the functions of a cell to the functions of organisms such as waste removal. 1. What type of cell in the human blood is responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body? Circle the correct answer: white blood cells or red blood cells. 2. What is the main function of the heart in our bodies? The hearts main function is to pump blood through our bodies. 3. List the characteristics of living organisms and cells. Refer to your notes on the functions of cells. The characteristics of living organisms and cells are to remove waste from themselves, grow and die, and extract energy from food. 4. What is the main function of the cilia and flagella in single celled organisms? The function of the cilia and flagella, in single celled organisms is for movement. 7.12F: Recognize that according to cell theory all organisms are composed of cells and cells carry on similar functions such as extracting energy from food to sustain life. 1. What do all living things have in common? All living things are made of cells. 2. What is the cell theory? The cell theory states that all organisms are composed of cells; the cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms, cells come from other cells by cell reproduction, and cell function. 3. In all living things, the presence of what structure supports the cell theory? The cell membrane supports the cell theory because all cells have a cell membrane that allows things to enter and leave the cell. 4. What are the four stages of mitosis? Refer to the picture of mitosis I gave you in your journal. The four stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.