* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Q24 Compare and contrast peptide and steroid hormones. Give four
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembling peptide wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
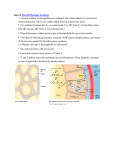
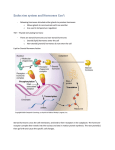
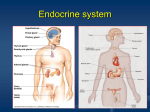
Q24 Compare and contrast peptide and steroid hormones. Give four examples of each (Sept 2012) Hormone -‐ a chemical substance produced by a specialized organ or gland, which enters the bloodstream and regulates the actions of other cells or organs. Peptide hormone Steroid hormone Examples Anterior pituitary hormones (LH, FSH, ACTH, Cortisol, aldosterone, oestrogen, TSH, GH), parathyroid hormone, insulin progesterone, testosterone Structure Range from small peptides (3-‐200 amino acids). Highly lipid soluble; consist of three cyclohexal Generally referred to as peptides if <100 amino ring and one cyclopental ring in a single acids, and proteins if >100. structure Synthesis Via transcription and specific messenger RNA in Synthesised from pregnenolone, a steroid the rough endoplasmic reticulum precursor (this is the rate limiting step) Precursor Synthesised as larger proteins (prehormones) Cholesterol then cleaved in the endoplasmic reticulum to form prohormones, and then cleaved in storage vesicles to form active fragments (hormones) Storage In secretory vesicles Minimal storage of the hormone itself, however large stores of cholesterol esters in the cytoplasm can be rapidly mobilized in response to a stimulus. Steroid hormones bound to plasma proteins also act as a reservoir. Transport Transported dissolved in plasma and then Circulate bound to plasma proteins diffuse into interstitial tissues at the target site Kinetics Mainly act on specific cell membrane receptors Readily enter cells to act on receptors in the and then via second messenger systems (cAMP, cell cytoplasm or nucleus, initiating G proteins, PIP system, calmodulin, tyrosine transcription of specific genes to promote kinase) to induce a cellular response ribosomal translation and protein synthesis. Judith Askew 2014