* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Simple Electrical Circuits
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Light switch wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
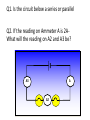
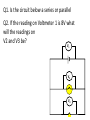
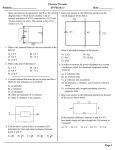
Simple Electrical Circuits Lesson 2-The Basics Recap Draw the circuit symbol for a bulb Draw the circuit symbol for an ammeter What component is used to measure electrical current? A. Switch B. Resistor C. Ammeter D. Voltmeter Which component changes electrical energy into light energy? A. Bulb B. Switch C. Cell D. Battery Which component is a store of chemical energy? A. Bulb B. Battery C. Switch D. Resistor Which of these materials is not a conductor of electricity? A. Water B. Graphite C. Lead D. Wood Name this circuit symbol. A. Ammeter B. Switch C. Bulb D. Voltmeter V Q1. Is the circuit below a series or parallel Q2. If the reading on Ammeter A is 2AWhat will the reading on A2 and A3 be? A A3 A2 Q1. Is the circuit below a series or parallel Q2. If the reading on Ammeter 4 is 2A what will the reading on: A2, A3 and A1 be? A1 A4 A2 A3 Q1. Is the circuit below a series or parallel Q2. If the reading on Voltmeter 1 is 8V what will the readings on V2 and V3 be? V1 NB Voltmeters are connected in parallel V2 V3 • For a series circuit, the sum of the voltages for each component is equal to the voltage across the cell or battery. • V1 = V2 + V3 Q1. Is the circuit below a series or parallel Q2. If the reading on Voltmeter 1 is 8V what will the readings on V2 and V3 be? V1 V2 V3 • For a parallel circuit, the voltage across the cell/battery is the same as the voltage across each branch. • V1 = V2 = V3