* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What does DNA stand for?
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
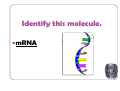
What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid _______ is the enzyme that chemically links Okazaki fragments together DNA Ligase What is located at the BOTTOM of a tRNA molecule? Anti-codon sequence Where in the cell is DNA found? Nucleus Scientifically, describe the shape of the DNA molecule. Double Helix What is a benefit of semiconservative DNA replication? Helps reduce the number of copying errors Why is transcription important? Gets the DNA code out of the NUCLEUS! What is located at the top of tRNA? Amino acid What are the 2 types of purines? Adenine, Guanine What is the complement to this side of a DNA molecule?: TGGACTA ACCTGAT How many pairs of chromosomes does a human have in their body cells? 23 How many hydrogen bonds are found between A-T? 2 Where can mRNA be found? Nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosome A segment of DNA that codes for a protein is called a ______ Gene What are the 3 parts of the DNA molecule? Phosphate group Deoxyribose Sugar Nitrogen Base ______is the DNA strand that is discontinuously built into small Okazaki fragments during replication Lagging Strand What sugar is present in RNA? ribose What type of replication occurs when DNA replicates? Semiconservative Replication ______________ are short segment of DNA synthesized discontinuously in small segments in the 3’-5’ direction by DNA polymerase. Okazaki Fragments What nitrogen bases are present in RNA? A, U, C, G What is chromatin? Uncoiled DNA What type of bond holds together the nitrogen bases? Hydrogen What scientists are credited with the “base-pairing” rules? Watson & Crick DNA that is coiled would be called? Chromosome When does the DNA replicate? Cell division/Interphase (before mitosis) In what direction can DNA synthesis only occur? 5’-3’ How many hydrogen bonds are found between C-G? 3 Going from mRNA to a protein is called _______. Translation During DNA replication, what causes the hydrogen bonds to break? An Enzyme (DNA Helicase) What is the tRNA complement to this mRNA?: AUGCAU UACGUA What is located at bottom of tRNA? Anti-codons Who discovered DNA in 1928? Frank Griffith What polymer makes up or hair color, bone length, etc..? Protein What is the shape of mRNA? Single helix What are the 2 types of pyrimidines? Thymine, Cytosine What is the function of tRNA? tRNA anticodons bond w/ mRNA codons to insure the correct order of amino acids _______ is the enzyme runs along the parent chain of DNA and bonds free floating nucleotides to those of the parent (original) chain-- based on base pairing rules DNA Polymerase What sugar is present in DNA? Deoxyribose What does RNA stand for? Ribonucleic Acid How many strands of mRNA are transcribed from the two “unzipped” strands of DNA? 1 What nitrogen bases are present in DNA? A, T, C, G How is the accuracy of the DNA code assured? Base-pairing rules _________ is the DNA strand that is continuously built by the addition of nucleotides to the 3’ end during replication Leading Strand Going from DNA to mRNA is called _________. Transcription What is the mRNA complement to this side of a DNA molecule: AACGTAT UUGCAUA How does the mRNA get out of the nucleus? Nuclear pore Identify this molecule. DNA What is located at the TOP of a tRNA molecule? Amino acids Where does translation occur? Ribosome What is the function of mRNA? To get the DNA code out of the nucleus What are proteins made up of? Amino acids Where must the mRNA attach before protein production can begin? Ribosome Where does transcription occur? Nucleus Identify this molecule. tRNA How many nitrogen bases make up a mRNA codon? 3 What type of bond is formed between amino acids during translation? Peptide bond Identify this molecule. mRNA What is the function of rRNA? Creates peptide bonds between the amino acids